
Embracing self-care is a core strategy for anyone dedicated to maintaining long-term recovery and containing setbacks. Self-care strategies for preventing relapse are necessary for sustaining health and wellness after rehabilitation. Proactive self-management includes regular exercise, sufficient sleep, and healthy dietary habits that fortify mental and physical resilience against potential relapse triggers. This paragraph also sets the stage for an in-depth exploration of practical self-care techniques that support recovery. These strategies help individuals manage stress, recognize early warning signs of emotional distress, and maintain a balanced lifestyle. Throughout this post, we will discuss how integrating simple self-care routines can profoundly impact one's ability to stay on the path of recovery, highlighting several methods to enhance well-being and prevent relapse effectively.
Understanding Relapse: A Key Step in Prevention
Relapse refers to the return to substance use after a period of abstinence, which can be a part of many people's long-term recovery process. Recognizing the triggers and stressors that lead to relapse is essential for anyone looking to maintain their sobriety. These triggers often include emotional distress, environmental cues linked to past substance use, or social pressures.
Self-awareness involves being conscious of the feelings and external situations that pose a risk for relapse. By acknowledging these warning signs early, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their responses to these triggers. It might involve seeking support from peers or counselors, engaging in healthy activities, or utilizing coping strategies learned during therapy. Increasing self-awareness helps individuals anticipate challenges and arm themselves with the tools needed to navigate them, maintaining their commitment to recovery.
Self-Care Strategies for Preventing Relapse
Implementing strategies that bolster physical and mental health reduces the risk of returning to old habits. Engaging in physical activities is a powerful tool for managing stress and enhancing overall health. Activities such as brisk walking, jogging, or swimming will improve cardiovascular health while boosting mood through endorphin release. Incorporating mental health practices like mindfulness and meditation into daily life is equally vital. These practices help center thoughts, reduce anxiety, and improve emotional regulation, creating a more resilient mindset capable of handling potential stressors that might trigger a relapse.
Furthermore, maintaining regular sleep patterns and adhering to a nutritious diet is essential for a comprehensive self-care regimen. Consistent, restorative sleep and balanced meals ensure that the body and mind are well-nourished and primed to tackle challenges, reducing susceptibility to stress-induced relapse. Together, these self-care strategies form a robust defense against relapse, fostering long-term recovery and stability.

Building a Support Network: Essential for Longevity
Building a robust support network is another critical component of self-care strategies for preventing relapse. Choosing the right support group or network can be transformative. Look for groups with similar experiences and recovery goals, as this alignment can provide more relevant advice and empathetic understanding. Family and friends' support can offer emotional comfort and practical help during challenging times. They should learn the best ways to support their loved ones in recovery. It may include participating in family therapy sessions or educational programs.
Additionally, using professional help is a cornerstone of a successful recovery strategy. Therapists and counselors trained in addiction recovery can offer guidance, monitor progress, and help navigate the complexities of maintaining sobriety. This professional support is essential for dealing with underlying issues that contribute to substance use and for learning new coping strategies to prevent relapse.
Avoiding High-Risk Situations
Being aware of the most common relapse triggers, such as exposure to substances, stress from interpersonal conflicts, or attendance at high-pressure social events, enables you to steer clear of potential pitfalls. Developing a keen sense of these triggers and the ability to predict high-risk situations before they occur will help you build a robust recovery strategy.
To manage temptations and avoid risky environments:
● Stay away from old haunts and routines: Alter your routes and habits that were part of your past substance use.
● Use refusal skills: Practice saying no in a convincing, respectful manner.
● Engage in alternative activities: Fill your time with hobbies and interests that do not involve substances.
Furthermore, having a solid exit plan empowers you to leave unsafe or uncomfortable situations without hesitation. This plan can be as simple as having a friend on call, knowing nearby safe locations, or even rehearsing reasons to leave risky scenarios.

Monitoring Progress and Setting Realistic Goals
Monitoring progress and setting realistic goals are fundamental to sustaining recovery and preventing relapse. Keeping a journal to track progress allows individuals to reflect on their successes and areas for improvement, providing a tangible record of their journey toward recovery.
Setting achievable and meaningful goals is crucial. Goals should be specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). For example, a goal might be to attend a support group meeting twice a week or to practice meditation for 15 minutes daily. These goals help structure daily life and give a sense of direction.
Celebrating milestones, whether big or small, acts as a motivational tool. Acknowledging these achievements boosts self-esteem and reinforces the value of the hard work put into recovery. Celebrations can be as simple as a quiet evening at home or as lively as a gathering with close friends or supporters.

Adapting Your Strategies Over Time
Adapting your strategies over time is crucial in maintaining effective self-care and preventing relapse. Recognizing when you need adjustments in your self-care plan allows you to remain aligned with your current needs and challenges. Life circumstances can change, and what works at one stage may not be as effective later. Be flexible and responsive to these changes to sustain recovery. Staying adaptable involves periodically reviewing your strategies and being open to modifying them. For instance, if your stress levels are increasing despite your current routine, it may be time to introduce new activities or support mechanisms that better address your needs.
Learning from setbacks without self-judgment is also vital. Viewing mistakes as learning opportunities rather than failures helps to foster resilience. It's important to approach these moments with kindness and understanding towards yourself, which encourages personal growth and helps prevent discouragement and relapse.
Conclusion
Maintaining balance and health is essential in making self-care strategies for preventing relapse, which is the ongoing process of recovery and relapse prevention. This article has highlighted critical self-care strategies for preventing relapse and supporting mental and physical well-being. Regular exercise, mindfulness practices, and a robust support network are just a few methods that can enhance your resilience. Finally, we encourage you to continue prioritizing these self-care measures, adapting them as your circumstances evolve. Start implementing these strategies today to strengthen your recovery journey. Your commitment to self-care is not just beneficial—it's necessary for a balanced and healthy life.

Living with depression can be challenging at any time of year. For people struggling with their mental health, the summer months can bring a unique set of obstacles. It is implied that summer is for enjoying the warmth of the sun and summer festivities. However, for individuals battling depression, they may find it difficult to find that same sense of lightness and happiness. In this blog post, we will explore how therapies like Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) and Internal Family Systems (IFS) can offer hope and relief for those suffering from depression, even in the midst of summer.
Understanding Depression in the Summer Sunlight
Summer often paints a picture of endless joy and outdoor celebrations. For those grappling with depression, this season can cast a shadow of heightened despair. The contrast between the societal expectation of summer bliss and the personal reality of inner turmoil can exacerbate feelings of isolation and inadequacy. During these warmer months, the pervasive cheerfulness can feel isolating to someone struggling internally. It can make the gap between their experience and that of others seem even wider. This disparity can intensify the sense of being out of place or left behind.
This may feel like the world around them seems to bask in a light that feels unattainable. Furthermore, the increased social activities and gatherings that characterize summer can serve as reminders of one's battles with social anxiety. It can add layers of complexity to an already challenging mental health landscape. The omnipresent cultural message that summer is a time for unfettered happiness can inadvertently place undue pressure on those who find their reality far removed from this idealized notion. This might turn what is meant to be a season of warmth and growth into a period of deepened struggle.
Celebrating Summer Festivities While Coping with Depression

Engaging in summer celebrations when dealing with depression may seem daunting. Despite that, small, intentional actions can create moments of joy amidst the struggle. Begin by acknowledging your feelings without judgment and permit yourself to participate in activities that feel manageable and comforting. Instead of succumbing to the pressure of attending large gatherings, consider smaller or more intimate settings where you feel safe and supported.
Creating a personal tradition or ritual that brings you peace and joy during the summer can also be a powerful step towards healing. This might be as simple as watching the sunrise, taking a walk in nature, or dedicating time to a hobby you love.
Additionally, harness the power of connection by reaching out to trusted friends or family members who understand your journey. Sharing your experiences with them can provide a sense of belonging and support, making the festivities less isolating. If direct participation feels too overwhelming, try to find alternative ways to engage with the spirit of summer. This can be planning a virtual get-together, or sitting outside to soak in the warmth and sights of the season.
Remember, it’s perfectly acceptable to decline invitations when you need time for yourself. Your well-being is paramount, and finding a balance that respects your mental health is crucial. Celebrating in a way that honors where you are on your journey can make the summer more enjoyable and meaningful.
An Overview of EMDR Therapy for Depression Treatment
EMDR (Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing) therapy stands as a transformative approach in the field of psychological treatment, particularly for depression. This innovative method harnesses the power of bilateral stimulation, such as side-to-side eye movements or tapping. This is to facilitate the processing of distressing memories and emotions that contribute to depressive states. The therapy sessions are structured to allow individuals to revisit traumatic or triggering events in a safe and controlled environment.
Through guided eye movements led by a trained therapist, patients can re-examine these experiences without the intense emotional response that they typically elicit. The aim is to desensitize the individual to these distressing memories. By reducing their impact, it allows for the development of healthier coping mechanisms. As a result, EMDR has been effective in mitigating the symptoms of depression, providing a pathway toward emotional healing and resilience. This therapy offers a beacon of hope for those seeking to overcome the effects of depression. It offers a way to reclaim a sense of mental freedom and well-being.
Exploring Internal Family Systems (IFS) as a Depression Treatment
Internal Family Systems (IFS) therapy emerges as an innovative and compassionate approach to tackling the complexities of depression. This therapeutic model delves into the multifaceted nature of the psyche. It proposes that the mind consists of subpersonalities, or "parts," each with its unique perspectives, feelings, and memories. IFS aims to identify and understand these parts, especially how they interact and sometimes conflict, contributing to depressive symptoms. Central to IFS therapy is the concept of the Self. The Self is a core aspect of being that embodies qualities such as confidence, clarity, and compassion. Through IFS, individuals learn to access their Self and lead their internal system with these qualities. Doing this offers comfort and guidance to parts in distress.
The process of IFS therapy involves engaging with these parts in a nonjudgmental and curious way, recognizing their positive intentions, and understanding the burdens they carry. These burdens typically stem from past traumas or negative beliefs. By healing these parts, IFS helps to release their burdens, allowing for a more harmonious internal system. This can lead to significant decreases in depressive feelings, as individuals are no longer weighed down by the conflicts and burdens within their parts. Through fostering an internal environment of understanding, compassion, and support, IFS therapy holds the potential to transform the internal landscape. It can offer relief and a pathway out of depression's depths.
The Challenge of Treatment-Resistant Depression
Treatment-resistant depression presents a profound obstacle, making the journey toward mental wellness seem insurmountable for some. Defined by a lack of response to traditional treatments, such as medication and standard talk therapies, individuals facing this form of depression may feel trapped in a cycle of unsuccessful attempts to find relief. This condition demands a more nuanced understanding of the underlying causes of depression. It urges a shift toward innovative and personalized therapeutic approaches.
The complexity of treatment-resistant depression lies in the persistence of symptoms and the unique experiences and histories of those affected. Recognizing this challenge is crucial in exploring alternative paths to healing. Delving deeper into the psychological roots of depression with therapies like EMDR and IFS can potentially be beneficial. For those grappling with this daunting form of depression, it's essential to maintain hope and continue seeking options that address the specific dimensions of their distress.
Can EMDR and IFS Offer Hope for Treatment-Resistant Depression?

For individuals navigating the challenging waters of treatment-resistant depression, traditional approaches may not always lead to the desired shores of relief and recovery. In these instances, EMDR (Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing) and IFS (Internal Family Systems) therapy stand out as potential lighthouses, offering guidance and hope. These therapies delve into the deeper layers of the psyche. They address the root causes of depression rather than just its surface symptoms. EMDR focuses on reprocessing traumatic memories that often underpin depressive disorders, allowing individuals to experience these memories in a less distressing way.
Meanwhile, IFS offers a path to understanding and healing the fragmented parts of oneself, fostering internal harmony and reducing depressive symptoms. By engaging with these innovative therapies, individuals with treatment-resistant depression may find avenues for change that were previously unexplored. The personalization and depth of EMDR and IFS can resonate with those who have felt misunderstood or untouched by other treatments. It provides a fresh perspective and renewed hope. As more research unfolds and clinical experiences accumulate, the potential of EMDR and IFS to significantly impact treatment-resistant depression becomes increasingly evident. It offers a glimmer of light to those who have long been in the shadows.
Practical Steps to Seek Help and Start Therapy
Taking action to address your depression by connecting with a professional can mark the beginning of your journey to wellness. To start, research therapists who specialize in depression and are trained in EMDR, IFS, or any therapy that resonates with you. Many resources are available online. This includes directories and reviews, to help you find a clinician who matches your needs and preferences. Don't hesitate to reach out and ask questions about their approach, experience, and how they've helped others with similar challenges.
Booking an initial consultation can provide insight into whether you feel comfortable with the therapist and their methodology. Remember, the therapeutic relationship is pivotal to the success of your treatment, so feeling understood and safe is essential. If the fit isn't right, it's perfectly fine to seek out another professional who better aligns with your expectations and needs.
Additionally, consider joining support groups, either in-person or online. Connecting with others facing similar struggles can offer validation, encouragement, and practical advice on navigating depression. Support groups also provide a sense of community and belonging, vital components in overcoming feelings of isolation.
Finally, be open to discussing your concerns with loved ones. While starting therapy is a personal decision, having the support of friends or family can bolster your resolve and provide an additional layer of support as you embark on this healing journey.

For many individuals in the LGBTQIA+ community, the journey of transitioning can be a tumultuous one. A journey filled with a range of emotions including anxiety and depression. The process of coming to terms with one's gender identity, undergoing hormone replacement therapy (HRT), and potentially having surgeries can be overwhelming. However, there is a therapeutic approach that may offer relief and help individuals feel more connected with their mind and body. It is called Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) therapy.
Understanding the Emotional Terrain of Transitioning
Transitioning, for many within the LGBTQIA+ community, represents not only a journey of physical metamorphosis but also of profound emotional exploration and self-discovery. This path, while ultimately affirming, is often fraught with complex feelings that can challenge even the strongest among us. As individuals embark on this deeply personal quest to align their outer selves with their inner truth, they may confront a myriad of societal pressures and internal conflicts that can exacerbate feelings of anxiety and depression.
The emotional landscape of transitioning is intricate and varied. It can encompass the excitement and hope of becoming more authentically oneself. It also comes with the fear and uncertainty that change inevitably brings. This anticipation of achieving congruence in one’s gender identity can be shadowed by the dread of potential isolation, misunderstanding, and discrimination. These external pressures compound the internal struggle, making it difficult for some to navigate the process of self-acceptance and self-love.

Complicating this journey further are the obstacles to finding affirming support and understanding. Misconceptions and stigma about what it means to transition can leave individuals feeling isolated and invalidated. This can intensify feelings of anxiety and depression. The daunting task of explaining one’s identity to others, fear of rejection, and the constant battle against societal norms and expectations can be overwhelming, leading to a profound sense of loneliness and despair.
As such, the emotional terrain of transitioning is marked by highs and lows. This can range from moments of exhilarating clarity as well as painful doubt. The process requires incredible resilience and courage, as individuals navigate through this complex emotional landscape in pursuit of their true selves. While the journey is inherently challenging, understanding and acknowledging these emotional experiences are crucial steps toward healing and growth.
An Introduction to EMDR Therapy
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) therapy emerges as a compelling psychotherapeutic approach. It is particularly renowned for its efficacy in addressing trauma-related conditions. EMDR facilitates the processing of distressing memories and emotional pain by activating both hemispheres of the brain through bilateral stimulation. This bilateral stimulation can be guided eye movements or tactile tapping. This innovative method aims to assist individuals in reorganizing and reinterpreting memories and emotions that are at the root of their psychological distress.
Developed in the late 1980s, EMDR has rapidly evolved and garnered empirical support as a treatment for various manifestations of psychological distress. Its unique methodology involves eight distinct phases, guiding clients from history-taking to the processing of traumatic events, and culminating in the consolidation of adaptive coping mechanisms. During EMDR sessions, therapists work closely with clients to identify specific distressing memories. They also help to identify negative beliefs about themselves that are associated with these memories. Through the structured phases of EMDR, clients are encouraged to focus on these memories while simultaneously engaging in bilateral stimulation. This dual focus facilitates the brain's natural healing process. This allows for the emotional charge of the memory to be diminished and for a more adaptive, empowering narrative to emerge.
Importantly, EMDR therapy goes beyond mere symptom relief, striving to foster a holistic sense of healing. Clients often report a decrease in distress related to specific memories and an overall improvement in their well-being. This gives room for an increased capacity to engage in their lives more fully. By directly targeting the underlying emotional impact of traumatic and distressing experiences, EMDR holds promise as a transformative therapeutic modality, especially for those contending with the profound emotional complexities associated with transitioning. Through its structured yet flexible approach, EMDR offers a pathway to healing that is both scientifically grounded and deeply attuned to the individual's psychological landscape.
EMDR in Action: Healing from Gender Dysphoria
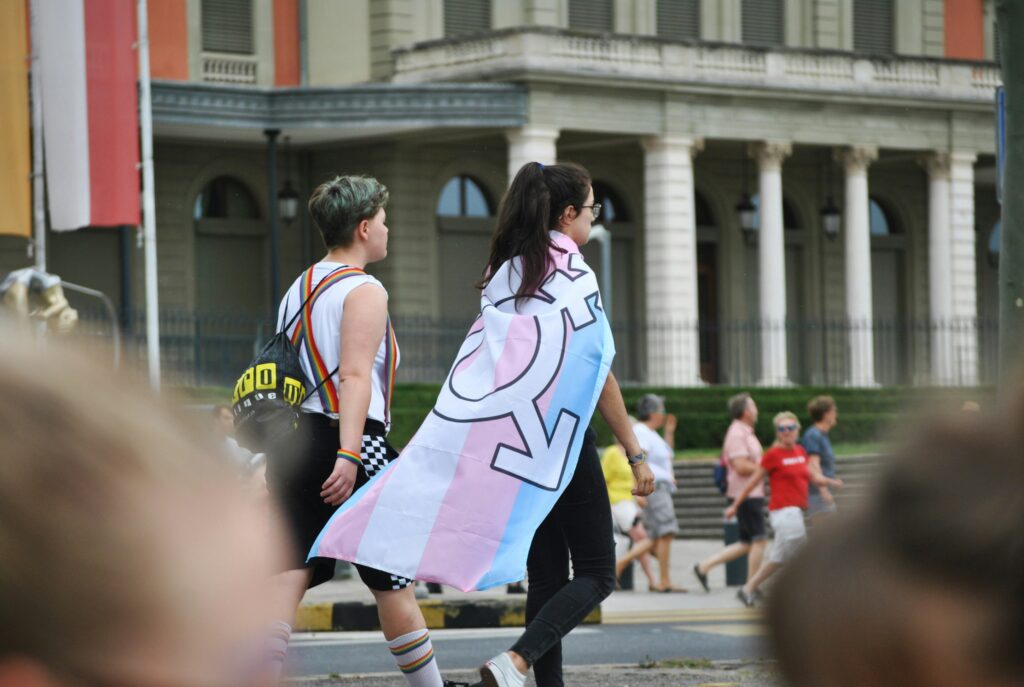
EMDR therapy emerges as a vital resource for those grappling with gender dysphoria. Gender dysphoria is a condition characterized by profound discomfort due to a discrepancy between one’s experienced gender and the gender assigned at birth. This discomfort often manifests as severe anxiety, depression, and a disconnection from one’s body. In navigating these turbulent emotions, EMDR offers a promising avenue for healing and self-discovery.
Through its structured approach, EMDR targets the distressing memories and negative self-perceptions that underpin gender dysphoria. Individuals may harbor deep-seated beliefs of not belonging, being misunderstood, or feeling inherently flawed due to their gender identity struggles. EMDR engages the brain’s natural healing processes, allowing individuals to reprocess these painful experiences and beliefs. By focusing on specific memories or thoughts while receiving bilateral stimulation, clients can start to dissociate the negativity, shame, or fear attached to these memories. It can pave the way for more affirmative and empowering narratives about their gender identity.
The therapy’s unique ability to delve into the layers of emotional pain and cognitive dissonance that accompany gender dysphoria makes it an invaluable tool. It assists in alleviating the acute distress associated with living in a body that feels incongruent with one’s gender identity. As these individuals process their experiences through EMDR, they often find that the emotional charge of their distressing memories diminishes. This reduction in emotional intensity can lead to a significant decrease in anxiety and depression levels. It can ultimately contribute to a more harmonious internal experience.
As part of a comprehensive treatment plan, EMDR facilitates a journey towards self-acceptance and body congruence. It helps individuals in the LGBTQIA+ community to not only reconcile their past experiences with their gender identity but also fosters a stronger, more positive connection with their bodies and selves. Through EMDR, the path to healing from gender dysphoria becomes more accessible. It, empowers individuals to embrace their true identity with confidence and peace.
The Role of EMDR in Overcoming Anxiety and Depression
EMDR therapy stands out as a potent intervention for mitigating the profound impacts of anxiety and depression. This is particularly poignant for those undergoing the transition process. This therapeutic modality dives deep into the psyche, addressing the root causes of these mental health challenges. Through the distinctive mechanism of bilateral stimulation, EMDR aids individuals in accessing and processing the distressing memories and entrenched negative beliefs that fuel their emotional turmoil.
In the context of transitioning, anxiety and depression often stems from accumulated life experiences, societal rejection, or internalized stigma. Each of the forementioned can create a pervasive sense of being trapped or misunderstood. EMDR facilitates a re-examination and restructuring of these painful narratives, allowing for a transformative healing journey. By engaging the brain's innate capacity for resilience and recovery, it offers a path through which clients can gradually diminish the intensity of their emotional pain. It makes room for more adaptive, positive perspectives on their identities and experiences.

The therapy’s focused approach enables individuals to dismantle the complex layers of anxiety and depression. This helps to foster a sense of empowerment and renewed self-compassion. As these individuals progress through the phases of EMDR, they often report a significant alleviation of their symptoms. People begin to experience an enhanced ability to cope with stress and embrace their true selves with greater confidence.
EMDR's role in combating anxiety and depression is thus pivotal. It offers not just a means to cope but a route to thriving. Its application within the transitioning journey underscores a commitment to holistic well-being. Doing this, acknowledges the intrinsic link between resolving past traumas. It truly fosters a future where one's gender identity can be lived fully and authentically.
Finding Support and Embracing EMDR Therapy
In the pursuit of healing and self-discovery during transitioning, the role of supportive therapy cannot be overstated. It is critical to connect with therapists who possess a deep understanding of gender diversity. It is just as important that they exhibit a genuine commitment to creating a respectful and welcoming therapeutic environment. EMDR therapy has the profound potential to address the psychological distress associated with transitioning. This requires navigating with a therapist is skilled in its application and sensitive to the nuances of the LGBTQIA+ experience.
Choosing the right therapist involves seeking out professionals who are conversant with EMDR and actively affirm and celebrate LGBTQIA+ identities. Such therapists are instrumental in fostering a space where individuals can explore their feelings and experiences without fear of judgment or misunderstanding. They play a crucial role in facilitating the therapeutic process, guiding individuals through the nuanced phases of EMDR with empathy and understanding.
Embarking on EMDR therapy with a supportive therapist opens up avenues for profound emotional healing and growth. This therapy is done in a manner that is both empowering and transformative. It enables individuals to work through the layers of anxiety, depression, and trauma that transitioning can unearth. The journey with EMDR therapy is one of reclamation, allowing individuals to rewrite their narratives with strength and authenticity.
The decision to seek out EMDR therapy, paired with the support of a knowledgeable and affirming therapist, marks a significant step towards achieving psychological well-being and a deeper alignment with one’s true self. It underscores the importance of supportive relationships in the healing journey, reminding individuals that they do not have to navigate this path alone.

Juneteenth, also known as Freedom Day or Emancipation Day, is a significant date in American history. It commemorates the end of slavery in the United States. On June 19th, 1865, Union soldiers arrived in Galveston, Texas, with news that the Civil War had ended and that all enslaved individuals were now free. This day represents not only the liberation of African Americans but also the recognition of their humanity and dignity. As we reflect on the importance of Juneteenth in our shared American history, it is essential to consider the role that therapy can play in honoring this day and fostering connection among all people.
The Historical Significance of Juneteenth
The celebration of Juneteenth marks a pivotal moment in the journey toward freedom and equality in the United States. Its roots can be traced back to a time when the promise of liberation was delayed for many, despite the legal proclamation of their freedom. The arrival of Union troops in Galveston, Texas, on June 19, 1865, signified the enforcement of the Emancipation Proclamation in one of the last Confederate strongholds. It brought the message of freedom to the remaining enslaved African Americans. This event did not just signal the end of slavery. It symbolized a new beginning and the arduous journey toward civil rights and recognition for African Americans.
The significance of Juneteenth extends beyond the date itself. It embodies the continued resilience and struggle of African Americans throughout history. Acknowledging this day provides a lens through which we can view and understand the historical context of racial injustice and the fight for equity that persists today. It prompts a reflection on the past, offering insights into the systemic barriers that have shaped the experiences of African Americans over generations. Juneteenth, therefore, stands as a testament to both the horrors of the past and the enduring spirit of hope and perseverance in the face of adversity. By commemorating this day, we not only pay homage to the trials and triumphs of African Americans. We also affirm our commitment to addressing the legacy of slavery and its impact on contemporary society.
Juneteenth in Contemporary American Culture

Juneteenth's emergence as a widely recognized and celebrated holiday in the United States. It is a testament to its growing importance in the tapestry of American culture. It serves as a moment of national reflection and acknowledges the deep-seated history and contributions of African Americans. Throughout the nation, Juneteenth is commemorated with vibrant expressions of joy, resilience, and cultural pride.
Parades that march through city streets, festivals that fill parks with the sounds of jazz, gospel, and blues, and educational events that promote a deeper understanding of African American history and achievements, all contribute to the rich observance of this day.
The culinary traditions associated with Juneteenth celebrations are particularly noteworthy. They feature foods that hold historical significance and are a nod to African American culinary heritage. These gatherings are not just a showcase of cultural expression but also an opportunity for communities to come together in a spirit of unity and reflection.
Book readings, film screenings, and spoken word performances further enrich Juneteenth events, offering insights into the enduring impact of slavery and the ongoing struggle for justice and equality. These contemporary cultural expressions are crucial for educating the broader public about the significance of Juneteenth and for inspiring a collective commitment to racial equity. Through such celebrations, Juneteenth not only honors the past but also shapes the present. It makes it an integral part of America's cultural landscape and a beacon of hope for future generations.
The Importance of Education and Awareness

Embracing the full legacy of Juneteenth necessitates a commitment to education and heightened awareness about the deep scars slavery has left on the fabric of American society. Educating ourselves and others about the harrowing experiences of those who were enslaved and their journey towards freedom is imperative. This journey towards knowledge is not merely about recounting historical events. It involves an in-depth exploration of the systemic racism that has pervaded various aspects of American life, affecting generations of African Americans. Through comprehensive education, from academic institutions to community forums and personal study, individuals can begin to understand the complex history of racial injustice in the U.S.
Awareness goes beyond historical education. It requires acknowledging the ongoing struggles against racial inequality and recognizing the resilience of Black communities throughout history. It involves challenging the narratives that have often been overlooked or minimized and highlighting the achievements and contributions of African Americans to the nation's history. Engaging with literature, documentaries, and other resources created by African American scholars and artists can provide valuable perspectives and foster a more inclusive understanding of American history.
This path of education and awareness is a vital component of honoring Juneteenth. It calls for an active participation in learning and dialogue. This encourages a reflective examination of one's own position within the structures of privilege and oppression. Through this informed lens, individuals can contribute to a more equitable society, embodying the spirit of Juneteenth in daily actions and interactions.
Therapy as a Bridge to Understanding

Therapy provides a vital space for deep personal reflection and growth around issues of race, privilege, and systemic injustice. It allows individuals to delve into their subconscious, uncovering and examining deeply ingrained biases that may not be immediately apparent. This exploration is crucial in the context of understanding and honoring Juneteenth. It fosters empathy and a more profound respect for the historical and ongoing struggles faced by African Americans.
Through therapeutic dialogue, clients are encouraged to confront uncomfortable truths about societal structures and their roles within them, facilitating a journey towards more conscious and equitable behaviors.
In sessions, therapists can guide individuals in navigating the emotional complexities that arise from learning about America's history of slavery and its lasting repercussions. This process is integral for those seeking to actively support racial justice but feeling unsure about how to contribute effectively. Psychotherapy offers tools for managing feelings of helplessness or guilt while empowering clients to engage in meaningful actions that honor the spirit of Juneteenth.
Moreover, therapy can help build resilience and a sense of agency in individuals directly affected by racial trauma. It providing a healing space to process experiences of discrimination and injustice. For communities and individuals alike, therapy acts as a crucial step towards collective healing, laying the groundwork for a society that truly understands and values the significance of Juneteenth. Through personal transformation and the development of empathy, therapy aids in bridging the historical divide. It can steer us towards a future marked by genuine understanding and respect across racial and cultural lines.
Collective Healing through Commemoration

Collective Healing through Commemoration is a crucial aspect of recognizing Juneteenth's value within our society. This day offers a unique opportunity for all Americans to engage in a process of mutual understanding and reconciliation. By participating in Juneteenth events, individuals from diverse backgrounds come together in a spirit of solidarity. Coming together to celebrate the progress made while acknowledging the work that remains in the fight against racial injustice. Such communal activities not only deepen our comprehension of the historical and cultural significance of Juneteenth but also reinforce our connections to one another. They serve as poignant reminders of the collective struggle for freedom and equality, echoing the importance of unity in diversity.
Through shared experiences, stories, and reflections, these gatherings become powerful venues for healing. They can offer spaces where communities can collectively mourn the atrocities of the past and celebrate the strides toward a more equitable future. Engaging in these acts of remembrance and celebration acts as a catalyst for ongoing dialogue and action. It pushes society toward the ideals of justice and freedom that Juneteenth embodies. This form of collective healing is essential for building a foundation of empathy and compassion that transcends individual experiences. It can foster an environment where true progress can be made in addressing the complexities of race and equality in America.
Actionable Steps to Honor Juneteenth
To meaningfully engage with Juneteenth, consider participating in or organizing educational events that spotlight African American history and culture. Such efforts can include book clubs focused on Black authors or film screenings of documentaries exploring African American experiences. It can also be discussions that bring to light the significance of Juneteenth. Volunteering with civil rights organizations or initiatives that address racial inequity can also amplify the impact of this day.
Embrace the power of social media to share information, resources, and personal reflections on the importance of Juneteenth. This can broaden awareness and encourage others to reflect on their role in promoting justice. Furthermore, creating art, music, or written work that celebrates African American achievements or reflects on the journey toward freedom and equality can serve as a powerful tribute to the spirit of Juneteenth. Engaging in these activities not only honors the historical essence of Juneteenth but also strengthens our collective commitment to a future where equality and justice are truly realized for all.

Pride month is a time of celebration, recognition, and unity for the LGBTQIA+ community and its allies. It is a time to honor the struggles and triumphs of those who have fought for equality. A time to continue the ongoing fight for acceptance and inclusion. As we delve into the significance of Pride month, let's explore what it means to be part of the LGBTQIA+ community, the role of allies, and how we can all come together to create a more connected and understanding world.
The Essence of Pride: More Than Just a Month
Pride month transcends the vibrant parades and rainbow flags that symbolize its celebration. At its core, it embodies a profound moment of collective reflection and acknowledgment for the LGBTQIA+ community. It's a period marked by a deep dive into the rich tapestry of LGBTQIA+ history, a history fraught with battles for rights, recognition, and the freedom to love and exist openly. It offers a moment to celebrate the victories and acknowledge the setbacks, understanding that the journey towards equality is ongoing and far from over.
Pride month is an opportunity to amplify the voices of the LGBTQIA+ community. It is to share stories of resilience, courage, and solidarity. It's a call to acknowledge the diversity within the community, recognizing that each individual's experience is unique, yet bound by a common struggle for acceptance and equality. This month serves as a reminder to engage with our identities fully and to claim spaces where we can express ourselves freely. It is when we can advocate for those still silenced by oppression and prejudice.
It's also a time for learning and growth, inviting individuals outside the LGBTQIA+ community to listen, learn, and participate in the movement towards a more inclusive society. Pride month challenges us to confront our biases and engage in meaningful conversations, and to extend our support to the ongoing fight against discrimination and inequality. It encourages us to look beyond the surface, to see the heart and soul of what Pride truly represents. It is a celebration of love, in all its forms, and a call to action for justice, today and every day.
Pride From the Perspective of an LGBTQIA+ Individual

For those of us within the LGBTQIA+ community, Pride holds a deeply personal significance. It is a time where our identities, often marginalized or misunderstood, are celebrated loudly and proudly. Pride serves as a poignant reminder of our resilience. It is a celebration of our ability to live openly and authentically in a world that hasn’t always welcomed us with open arms. It's about embracing every part of who we are, the struggles and the triumphs, and sharing that pride with the world.
For those of us within the LGBTQIA+ community, Pride holds a deeply personal significance. It is a time where our identities, often marginalized or misunderstood, are celebrated loudly and proudly. Pride serves as a poignant reminder of our resilience. It is a celebration of our ability to live openly and authentically in a world that hasn’t always welcomed us with open arms. It's about embracing every part of who we are, the struggles and the triumphs, and sharing that pride with the world.
For many, Pride is a testament to personal growth and self-acceptance. It's a journey of understanding and loving oneself, sometimes against formidable odds. It represents a collective defiance against attempts to erase or diminish our existences, and a celebration of the progress made, while acknowledging the work that remains.
Engaging in Pride activities, whether through parades, protests, or intimate gatherings, feels like joining a chorus of voices that resonate with a shared experience. It’s in these moments of unity and celebration that we find a powerful sense of belonging.
Yet, Pride is not only about the outward expressions of celebration and protest. It's equally about the quiet moments of reflection on one’s identity, the internal battles fought and won, and the personal declarations of self-worth and dignity. It’s an affirmation that our lives, our loves, and our stories matter and deserve recognition.
In essence, Pride from the perspective of an LGBTQIA+ individual is a rich tapestry of personal and collective narratives, woven together by the threads of courage, love, and unwavering hope for a future where everyone can live freely and authentically.
The Role of Allies During Pride Month

Allies to the LGBTQIA+ community possess a unique and invaluable position during Pride Month. They offer support, amplification, and advocacy that can significantly impact the atmosphere of acceptance and understanding. The presence and active participation of allies can underscore the universal message of Pride. That message is equality, love, and respect for all, irrespective of sexual orientation or gender identity. Allies can contribute by educating themselves about the history, challenges, and achievements of the LGBTQIA+ community, thereby fostering a deeper connection and empathy.
Allies can demonstrate their commitment to the cause of equality in many ways. Engaging in conversations, attending Pride events, and showing solidarity on social media and in daily interactions are some ways. This active involvement not only provides tangible support but also inspires others to reflect on their own attitudes and beliefs. This can potentially lead to a broader cultural shift towards inclusivity. Respectful curiosity and a willingness to listen are key attributes of effective allyship. Asking questions, seeking out resources to better understand the complexities of LGBTQIA+ experiences, and acknowledging one’s own privileges can pave the way for more meaningful support.
Moreover, allies have the power to influence their own circles. They can challenge homophobic and transphobic remarks or behaviors and advocate for LGBTQIA+ rights in personal, professional, and public spheres. Their role is not to overshadow or speak over the voices of LGBTQIA+ individuals but to stand with them. They can lend their support to amplify the messages of Pride and push back against inequality. Through these concerted efforts, allies help to build bridges, encourage dialogue, and contribute to the creation of a more accepting and compassionate society.
Navigating the Challenges: Mental Health and Inclusion

Navigating the complexities of mental health and inclusion presents a vital front in the journey towards a more accepting society for LGBTQIA+ individuals. The shadow of stigma and discrimination often casts a long and heavy burden on the mental well-being of community members. This might manifest in elevated rates of depression, anxiety, and feelings of isolation. Addressing these challenges necessitates a concerted effort from both the community and its allies to forge environments that are not just physically safe, but emotionally nurturing and inclusive.
Creating these spaces involves a multi-faceted approach. This includes advocacy for comprehensive mental health services that are sensitive to the unique needs of LGBTQIA+ individuals. It calls for an increase in representation across all sectors, ensuring that LGBTQIA+ voices are heard and validated in discussions about mental health. Additionally, fostering an atmosphere of open dialogue and education can help dismantle the harmful stereotypes and misconceptions that contribute to the societal stigma impacting mental health.
Engagement in these efforts is crucial. It signals to those grappling with mental health challenges that they are not alone. That their experiences are valid, and that there is a community ready to support them. By prioritizing mental health and inclusion, we can take significant strides towards alleviating the isolation and distress felt by many, paving the way for a future where every individual can thrive.
Fostering Connection and Understanding Across All Walks of Life
To bridge the divide between diverse communities, active engagement and open-hearted dialogue are pivotal. Encouraging empathy through shared experiences and stories allows us to see beyond our differences. It can uncover the common humanity that binds us. It’s through these personal connections that misconceptions can be dispelled and biases challenged. Participating in community events, volunteering for LGBTQIA+ causes, and being present in spaces that advocate for equal rights are practical steps anyone can take to deepen their understanding.
Furthermore, creating platforms for marginalized voices and ensuring these narratives are both heard and respected is crucial in fostering a culture of inclusivity. This effort requires a willingness to step out of one’s comfort zone and question the status quo. It is to actively listen with the intent to understand, not to respond. Through such actions, we weave a stronger social fabric. A fabric that is rich with diversity yet united in its quest for acceptance and equality. Engaging in this process not only enriches our own lives but also contributes to a broader societal transformation. This can pave the way for a future where everyone is celebrated for who they are.
Celebrating Pride While Staying True to Oneself
Celebrating Pride Month is an affirmation of our diverse identities and the vibrancy they bring to the collective human experience. It’s a period where the emphasis is on the valor to be oneself amidst a world still grappling with acceptance and understanding. Embracing our uniqueness becomes a powerful declaration of self-love and respect during this time. It is an invitation to honor our journeys, recognizing the courage it takes to live authentically in a society that often challenges our existence.
Engaging in Pride, therefore, means more than just participating in festivities. It's about internal reflection on the significance of our identities and the pride we carry in them. It's a call to acknowledge our worth, to celebrate our resilience, and to stand in solidarity with others who share our struggles and dreams. As we navigate through Pride Month, let's commit to fostering environments where everyone feels seen, heard, and valued. Let this be a time where we champion our rights, advocate for those still fighting for their voice. Remember that being true to ourselves is the ultimate act of resistance and celebration. Together, through understanding and embracing our unique stories, we contribute to a richer, more inclusive world.

As parents, we always want what's best for our children. We strive to provide them with a loving and nurturing environment. Sometimes, despite our best efforts, our children may need extra support. Therapy for children can be a valuable tool in helping them navigate challenges and develop coping skills. In this blog post, we will discuss when to take your child for therapy, signs your child might need therapy, and how parents can be involved in the therapeutic process without getting in the way.
Understanding the Role of Therapy in Children's Lives
The purpose of therapy for children extends far beyond mere conversation. It's a structured environment where young ones can explore their innermost feelings, thoughts, and behaviors under the guidance of a trained professional. This safe space is instrumental in helping them face various challenges, ranging from academic pressures to personal struggles. Through therapeutic engagement, children acquire valuable skills that aid in emotional regulation, enhance resilience, and foster a positive self-image. These skills are foundational to their ability to adapt and thrive in different situations they encounter as they grow.
Therapy also acts as a bridge, connecting children to their potential by unlocking avenues for personal growth and self-discovery. It's a place where their voices are heard and validated, which is crucial for building trust and openness. Therapeutic sessions are tailored to the child's age, developmental stage, and unique needs. It ensures that the interventions are both accessible and engaging. Activities may include play, art, or conversation, each serving as a medium through which children can express themselves freely and creatively. By nurturing these expressions, therapy contributes to their overall well-being. It can prepare them for the complexities of life with confidence and adaptability.
Key Indicators Your Child Might Need Professional Support

Identifying the right moment to seek therapy for your child often requires astute observation of their behaviors and emotional responses. Notable signs that may indicate the need for professional support include a marked shift in mood or demeanor. This could be an unusual increase in irritability, sadness, or anger. You might also observe your child struggling with managing stress, displaying an overwhelming sense of worry or fear that doesn’t align with the usual ups and downs of childhood. Another red flag is a significant change in their eating or sleeping patterns. This can be symptomatic of deeper emotional turmoil.
Social withdrawal is another critical indicator. If your child is suddenly less interested in spending time with friends or participating in activities they once enjoyed, it could signal distress. Academic performance can also be affected. This can be seen as declines in grades or a reluctance to attend school potentially pointing to underlying issues. Additionally, an increased sensitivity to rejection or failure, manifesting in either aggression or retreat, can be a tell-tale sign of emotional struggle.
These indicators, particularly when persistent or intensifying, suggest that your child could benefit from the professional support therapy offers. Observing any combination of these behaviors warrants a closer look and potentially initiating a conversation about therapy, keeping in mind the child's overall well-being and the potential benefits of early intervention.
Common Misconceptions About Therapy for Children
Many parents harbor misconceptions about therapy for children that can hinder them from seeking timely help for their little ones. A prevalent myth is the belief that therapy is a sign of failure on the parent's part, suggesting they haven't managed their child's issues effectively. This misconception couldn't be further from the truth. Therapy is a proactive step toward understanding and resolving a child's challenges, emphasizing strength and resilience rather than failure.
Another widespread misconception is that children are too young to benefit from therapy. People often underestimate children's capacity to experience and communicate complex emotions. With the right approach, even young children can express themselves. They can gain insight from therapeutic interventions designed specifically for their developmental level.
There's also a belief that discussing problems in therapy might encourage negative behavior or exacerbate issues. On the contrary, therapy provides a controlled environment where children learn to articulate their feelings and develop healthy coping mechanisms. This safe exploration can prevent problems from escalating and teach children valuable life skills.
Lastly, some think therapy will make children dependent on professional support for life. In reality, therapy aims to equip children with the tools they need to navigate their emotions and situations independently. It fosters long-term resilience and emotional health. Addressing these misconceptions can open pathways to healing and growth for many families.
The Right Time to Seek Therapy for Your Child

Deciding the optimal moment to initiate therapy for your child can be nuanced and deeply personal. Observing persistent or escalating concerns in their behavior, emotional well-being, or social interactions can be significant indicators. Such signs might include uncharacteristic mood changes or heightened anxiety. It can also be difficulty in coping with daily stresses, or a noticeable decline in academic performance. It's important to acknowledge these signals without delay, as early engagement with a therapeutic process often leads to more effective outcomes.
Recognize that as a parent, your intuition about your child’s needs is valuable. If you observe behaviors or emotional states in your child that cause concern, it may be an indication to explore therapeutic options. Ultimately, the decision should be guided by a desire to support your child in achieving a healthier, more balanced state of well-being. Engaging in therapy should be viewed as a proactive measure, not a last resort. It can be a pivotal step towards fostering resilience and emotional health in your child.
How Parents Can Be Involved in Their Child's Therapy
Engagement and cooperation from parents are instrumental in enhancing the effectiveness of therapy for children. One of the primary ways parents can contribute is by establishing and maintaining an open line of communication with the therapist. This doesn’t mean infringing on the confidential space of the child’s therapy sessions. It means, staying informed about general progress and ways to support therapy goals at home. Following the therapist's guidance, parents can integrate specific strategies into daily routines. This can reinforce the skills their child is developing during sessions.
Being an active participant also involves educating oneself about the child’s challenges and the therapy process. Attending parent-focused sessions or workshops, when available, can provide valuable insights into understanding and managing your child’s needs more effectively. Additionally, creating a supportive home environment that mirrors the principles taught in therapy encourages consistency. It also aids in the child’s adaptive learning.
Moreover, it's crucial for parents to model healthy coping mechanisms and emotional expression. Children often learn by observing the behavior of adults in their lives. This makes it important for parents to demonstrate resilience and positive problem-solving in their own lives. Engaging in these practices not only assists the child's therapeutic journey but also fosters an atmosphere of mutual growth and learning within the family.
Preparing Your Child for Therapy

Introducing your child to the concept of therapy can be approached with sensitivity and openness. It's important to frame therapy as a positive and empowering step towards feeling better, rather than as a consequence of something being wrong. Use age-appropriate language to explain that the therapist is someone they can talk to about their feelings, thoughts, and anything that might be bothering them, in a place where it's safe to explore those feelings. Highlight that, like going to a doctor when we're physically sick, therapists help us when our feelings or thoughts need attention. Like a feelings doctor!
Encourage your child to view this as an opportunity to learn more about themselves and develop strategies to handle challenging emotions or situations. You can also alleviate any worries by discussing the structure of therapy sessions. This emphases the engaging activities they might do, like drawing or playing, which help in expressing themselves. Preparing them with reassurance and positivity paves the way for a more receptive and less apprehensive start to therapy.
Choosing the Right Therapist for Your Child
Selecting an appropriate therapist is a pivotal step in ensuring your child's therapeutic journey is both positive and impactful. Start by seeking a professional who is not only qualified but also specializes in pediatric mental health. Their expertise in dealing with children’s issues will be beneficial for addressing your child’s specific needs. Compatibility between your child and the therapist is also crucial; a therapist who resonates well with your child's personality and unique challenges can significantly enhance the therapy's effectiveness. Make an effort to understand the therapeutic methods being proposed. Therapists may employ various approaches, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, play therapy, or others, depending on what they believe will best suit your child.

It’s advantageous to solicit feedback from your child after initial sessions. This can provide insights into how comfortable and understood they feel, which are key indicators of a fruitful therapeutic relationship. Furthermore, ensure that the therapist’s logistical details, like location and availability, align with your family's schedule and needs to facilitate a consistent therapy schedule.
Transparency regarding the therapy process and expected outcomes is also vital. A therapist who communicates openly with you about your child's progress and strategies for support outside of sessions can greatly contribute to a cohesive approach to your child's well-being. In essence, finding the right therapist involves a blend of professional qualifications and personal compatibility, underlined by a mutual commitment to your child's mental health journey.

In today's digital age, teaching has become more challenging than ever before. With the rise of millennial parenting styles and the prevalence of social media addiction across all age groups, educators are facing unprecedented levels of stress and burnout. Fortunately, Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) therapy offers a promising solution to help teachers cope with the demands of their profession and support their students in navigating the complexities of modern education.
The Landscape of Modern Education and Millennial Challenges
The transformation of the educational environment in recent years has been profound, significantly influenced by the distinctive child-rearing practices of millennial parents. This generation of parents, having grown up with technology at their fingertips, often adopts a tech-savvy approach to parenting. This emphases open lines of communication and a partnership-oriented relationship with educators. However, this dynamic can lead to complexities in the classroom, as teachers strive to balance the digital-first expectations of millennial parents with the traditional educational values and practices.
Additionally, the millennial emphasis on individualized attention and customized learning experiences for their children can place added pressure on educators. People, who must navigate these demands while addressing the diverse needs of their entire student body. This shift has not only changed the way educators teach but also how they interact with parents. It requires new strategies and approaches to foster effective partnerships and promote student success in an ever-evolving educational landscape.
Understanding Social Media Addiction Across Ages

Social media's grasp extends far beyond a simple distraction. It weaves into the very fabric of students' lives across various age groups, cultivating an environment ripe for addiction. This pervasive issue sees young minds constantly battling for concentration amidst a barrage of notifications and digital interactions. It significantly impairs their academic capabilities and focus.
The allure of likes, shares, and instant communication holds a compelling sway, leading to a reduction in meaningful, face-to-face interactions and a dependency on digital validation.
Such addiction does not merely hinder educational outcomes. It also seeps into the mental health arena, potentially exacerbating feelings of isolation, anxiety, and depression among students. This complex web of digital engagement requires educators to adopt nuanced strategies to mitigate its impact. This encourages healthier online habits and fostering environments that prioritize both academic and emotional growth. In addressing social media addiction, the goal is to reclaim the attention and well-being of students, guiding them towards balanced, responsible use of technology.
The Psychological Toll on Educators

Navigating the dual pressures of millennial parenting expectations and the pervasive influence of social media, educators are enduring a significant psychological toll. The constant endeavor to balance digital-first approaches with traditional teaching methodologies. This, coupled with the need to engage students deeply entrenched in the digital world, places a unique strain on teachers. This relentless pressure exacerbates stress, propelling many towards feelings of anxiety and burnout.
Such emotional and mental fatigue not only impairs their capacity to provide high-quality education but also affects their personal well-being. The intensity of these challenges often leaves educators seeking strategies to safeguard their mental health while maintaining their commitment to fostering an enriching learning environment. In this milieu, the necessity for supportive interventions and coping mechanisms becomes paramount. It highlights the need for resources that can aid in managing the intricate dynamics of modern education.
Introduction to EMDR Therapy
EMDR therapy stands as a transformative approach within the therapeutic world. It is designed to aid individuals in processing and overcoming trauma, anxiety, and stress-related symptoms. This method employs bilateral stimulation, through eye movements or tactile tapping. It is a mechanism to facilitate the brain's processing of distressing memories and beliefs that contribute to emotional discomfort. Originating as a treatment for PTSD, its applications have broadened, showing effectiveness in addressing a range of psychological stressors. EMDR's unique capacity to accelerate the mind's natural healing processes presents a novel avenue for educators and students alike, grappling with the pressures of modern educational environments and digital disruptions.
Through targeted sessions, participants can experience relief from psychological burdens. It can pave the way for enhanced coping mechanisms and a renewed sense of mental clarity. This foundation in EMDR therapy elucidates its potential as a supportive tool in educational settings, aimed at ameliorating the emotional and cognitive challenges faced by today’s teachers and learners.
EMDR Therapy for Students

EMDR therapy holds significant potential for students ensnared in the challenges of navigating a digital-centric lifestyle and the stressors inherent in modern academic environments. This therapeutic approach is particularly adept at addressing the deep-seated psychological effects of social media overuse. This often manifest as heightened anxiety, decreased self-esteem, and impaired focus. Through the process of bilateral stimulation, students are guided to confront and reprocess negative beliefs or traumatic experiences that may be exacerbating their reliance on digital validation and hindering their academic and social development.
By integrating EMDR into student support services, educational institutions can offer a proactive pathway for students to break free from the cycle of digital dependency and its accompanying mental health issues. This not only aids in enhancing their emotional regulation and resilience but also cultivates a healthier relationship with technology. As students learn to manage their emotional responses and build a stronger sense of self-worth independent of online feedback, they're better equipped to engage fully with their educational journey.
Such therapeutic interventions can be instrumental in reorienting students toward more productive coping mechanisms. This encourages a shift from virtual spaces to real-world connections and learning. The adoption of EMDR therapy for student support underscores a commitment to nurturing not only the intellectual but also the emotional and psychological well-being of learners. It prepares them for a balanced and successful path through school and into adulthood.
Implementing EMDR in Educational Settings
The integration of EMDR therapy within schools represents a strategic approach to addressing the psychological challenges facing today's educational community. Key to this implementation is the professional development of educators and school mental health professionals, and equipping them with the skills necessary to facilitate EMDR techniques. Providing access to EMDR-trained therapists on campus can greatly enhance the support system available to both teachers and students.
Additionally, developing partnerships with local mental health organizations can expand resources and ensure a broad spectrum of support. Workshops and informational sessions could be organized to demystify EMDR therapy for the school community. It can highlight its benefits and potential to improve academic and emotional outcomes. By fostering an environment that values mental health as much as academic achievement, schools can cultivate resilience and well-being across their populations. This will empowers educators and learners to navigate the complexities of the digital age with confidence and support.
Conclusion and Moving Forward
The challenges presented by the intersection of millennial parenting, media addiction, and the demands of modern education require innovative solutions. EMDR therapy represents a powerful tool in this quest. It offers both educators and students a pathway to better mental health and resilience. As we look to the future, the importance of integrating psychological well-being strategies into the fabric of our educational systems cannot be overstated. Schools must become places where mental health resources, like EMDR, are readily accessible to address the complexities of today's digital and educational landscapes.
By equipping our teachers with the means to manage stress and burnout effectively, and providing our students with the skills to navigate their digital world healthily, we set the stage for a more positive and productive learning environment. The journey ahead will require commitment, collaboration, and open-mindedness from all stakeholders in the educational community. Embracing EMDR therapy as part of a comprehensive approach to mental health in schools is a critical step toward fostering an environment where everyone can thrive amidst the challenges of the 21st century.

Trauma is a powerful force that can shape our behaviors, thoughts, and emotions in profound ways. For many individuals, past experiences of trauma can manifest in various parts of their psyche. This can influence how they interact with the world around them. Internal Family Systems Therapy (IFS) offers a unique approach to understanding and addressing these internal parts, helping individuals navigate their inner world with compassion and curiosity. By delving into the core concepts of IFS, we can uncover the transformative power of recognizing and integrating these parts for holistic healing and self-acceptance.
Unpacking the Core Concepts of Internal Family Systems Therapy
Internal Family Systems Therapy (IFS) introduces a compelling framework for understanding the mind's landscape. At its core, IFS posits that the psyche is composed of multiple sub-personalities, or "parts." These parts each have their distinct roles, perspectives, and attributes. They, but are not limited to, protectors, managers, and exiles. Protectors are often tasked with shielding the individual from pain and vulnerability. Managers attempt to control behavior and external relationships to avoid hurt or disappointment. Exiles carry the emotional burdens and traumas that the system has deemed too overwhelming or dangerous to confront directly.

The interaction between these parts can significantly influence an individual's behavior, emotional responses, and patterns of thinking. In navigating through the IFS process, individuals learn to identify and understand the specific roles these parts play. They learn how the parts contribute to complex coping mechanisms forged in response to trauma and stress.
A pivotal aspect of IFS is fostering a non-judgmental curiosity about these parts. This leads to a deeper understanding of their intentions, fears, and desires. This empathetic inquiry enables individuals to form a compassionate connection with their parts, rather than engaging in internal conflict or attempting to banish these aspects of themselves. The ultimate aim is to harmonize the internal system, allowing the individual's true Self—a concept referring to the person's core essence characterized by qualities such as calmness, curiosity, compassion, and confidence—to lead and bring about healing and equilibrium.
Through IFS, individuals embark on a transformative journey. This can cultivate a relationship with their inner parts that is rooted in understanding, acceptance, and healing. This therapeutic exploration encourages the integration of all parts, facilitating a path toward greater self-awareness and emotional well-being.
The Significance of Recognizing Internal Parts

Acknowledging the multitude of parts within our internal system unveils a rich tapestry of emotions, motivations, and desires. This drives our behavior and shape our reactions to the world around us. This intricate exploration into our inner selves is fundamental in the journey toward self-awareness and emotional maturity. By inviting each part to communicate its story, fears, and aspirations, we unlock a deeper dimension of understanding that transcends surface-level interactions with our psyche. This empathic engagement with our parts encourages a transformation from within. It is where the once fragmented aspects of our identity begin to coalesce into a more unified and harmonious whole.
Recognizing these internal parts also demystifies the reasons behind certain behaviors or emotional responses that may have previously seemed irrational or unfounded. It offers a clarifying lens through which we can view our actions, revealing the protective or defensive roles these parts play. This revelation not only fosters a climate of self-compassion but also equips us with the knowledge to navigate our internal world more effectively. We learn to approach each part with curiosity and kindness, valuing their presence as integral to our holistic well-being. This process, though nuanced and layered, is instrumental in cultivating a balanced and authentic self-relationship. It lays the groundwork for profound personal growth and healing.
Addressing Trauma Through the Lens of IFS

When we approach trauma through the insightful perspective of Internal Family Systems Therapy, we unlock a profound avenue for understanding and healing. Trauma, by its nature, disrupts our internal equilibrium, often leaving parts of us in distress. IFS provides a structured yet flexible framework for engaging with these parts, many of which harbor the pain and fear from traumatic experiences. Through the IFS model, individuals learn to identify and interact with these parts—be it protectors who work tirelessly to shield us from further harm, or exiles carrying the weight of our pain.
This therapeutic process involves gently uncovering the stories and burdens these parts hold, acknowledging their presence, and validating their experiences. It's through this compassionate acknowledgment that individuals can begin to ease the grip of trauma. The parts that were once isolated or in conflict can be understood and honored for their roles. This allows for a reorganization of the internal system that promotes healing and resilience.
In the safety of the therapeutic relationship, individuals are guided to lead with their Self. The Self being the core of calmness and clarity within. This self-leadership is pivotal in fostering a nurturing internal environment where parts feel seen and heard. This reduces their need to engage in extreme roles or behaviors. By reestablishing trust within the internal system, trauma's hold can be loosened. It can pave the way for resilience and a renewed sense of wholeness. Through IFS, healing from trauma transcends mere coping, evolving into a journey of self-discovery and empowerment.
The Role of Self-Leadership in Healing and Transformation

At the foundation of Internal Family Systems Therapy is the empowering principle of self-leadership. This concept emphasizes the significance of steering one’s inner world through the strength and guidance of the Self. It embodies the essence of compassion, clarity, and calmness. Cultivating self-leadership is vital for individuals seeking to heal and transform their lives. It can foster an environment where the internal parts can find harmony and peace under the direction of the true Self. This journey of self-leadership encourages individuals to embrace their ability to guide and support their parts with understanding empathy. This leads to profound shifts in how they relate to themselves and navigate their emotional landscapes.
In the process of engaging with and leading one's parts, an individual discovers the capacity to face life’s adversities with a newfound resilience and insight. This approach not only alleviates the distress of the parts but also promotes an internal alignment that propels the individual toward positive change and personal evolution. The practice of self-leadership is a transformative endeavor that positions the Self to be the beacon of hope and healing. It guides the individual through the complexities of their internal world and toward a path of self-discovery and enduring growth. Emphasizing the role of the Self in this capacity underlines the transformative power of leading from a place of inner strength and authenticity, essential for achieving a state of balance and well-being.
Real-Life Applications of IFS in Addressing Repetitive Patterns

Exploring the practicality of Internal Family Systems Therapy reveals its efficacy in unraveling and transforming deeply entrenched behavioral patterns. Individuals often find themselves caught in a loop of repetitive actions and responses that seem resistant to change. These patterns, whether manifesting as procrastination, aggression, or withdrawal, have roots in parts that developed strategies to protect the self from harm or emotional pain.
Through the lens of IFS, individuals gain insights into the origin stories of these parts. They start to understand their protective intentions and the contexts in which they were formed.
The process begins with identifying the parts involved in these patterns. This includes, acknowledging their efforts to protect, and exploring the historical trauma or experiences that led to the adoption of such strategies. This awareness creates a platform for compassion and empathy towards oneself, facilitating a dialogue between the Self and its parts. Techniques such as direct access, where individuals communicate internally with their parts, and unblending, the separation of the Self from its parts to reduce overwhelming emotions, are instrumental in this process.
As individuals learn to lead with the Self, they can negotiate new roles for their parts. They can begin to move away from destructive patterns. This can enable them to move towards behaviors that are in alignment with their true values and goals. This shift does not happen overnight but is a gradual process. The process is of healing and reorganization within the internal family system. It ultimately leads to more adaptive and fulfilling ways of being in the world.
Embracing Self-Acceptance and Integration for a Fulfilling Life

The essence of Internal Family Systems Therapy lies in its capacity to facilitate a profound embrace of every facet of one's being. As individuals journey through the process of identifying and engaging with their varied internal parts, a transformative shift toward self-acceptance begins to unfold. This path of integration is marked by an intentional and compassionate acknowledgment of each part's existence and its contribution to the individual's life narrative.
The realization that these parts, regardless of their roles, are fundamentally aimed at self-preservation and protection. It allows for a softening of internal resistance and a welcoming of all aspects of the self. Such a holistic embrace fosters a deep sense of completeness and unity within. It sets the stage for living in alignment with one's authentic self. As this internal harmony is achieved, individuals find themselves better equipped to face life's challenges with a resilient and grounded presence. This leads to a life that is not just endured but richly experienced and enjoyed.

In the realm of family dynamics, the role of fathers has often been overshadowed by the traditional notion that their primary duty is to provide financial support. This limited perspective underestimates the value that fathers bring beyond their wallets, leaving mothers to bear the weight of full-time jobs and childcare responsibilities alone. This skewed expectation not only overburdens mothers but also sends damaging messages to our children about gender roles and relationships. It's time to shed light on the critical role of fathers in child-rearing and household responsibilities. To challenge the outdated belief that active paternal involvement compromises masculinity.
The Evolution of Fatherhood in Family Dynamics
As society's norms and expectations have progressed, so too has the perception and reality of fatherhood within family dynamics. The traditional image of the father as merely a provider has transformed, giving way to a more comprehensive view that encompasses emotional, mental, and physical involvement. This transformation acknowledges fathers as crucial figures for emotional support, guidance, discipline, and active participation in day-to-day childcare. The evolution is partly driven by the changing landscape of the workforce, with more mothers entering full-time employment, thereby necessitating a shift in domestic roles. Additionally, a growing body of research underscores the positive impact of father engagement on child development, challenging old paradigms and encouraging a new generation of dads to embrace a hands-on approach to parenting.
This shift away from rigid gender roles towards a more egalitarian model not only enriches the father-child relationship but also contributes to a more balanced distribution of household and parenting responsibilities. As we continue to navigate these changing dynamics, it becomes clear that the modern father’s role is as much about emotional nurture and participation in the home as it is about providing financial support, marking a significant step towards a more inclusive understanding of fatherhood in today's world.
Unpacking the Financial Provider Stereotype

The stereotype that fathers primarily serve as financial providers has deep roots, yet it confines their role to a singular dimension that overlooks their broader impact on family life. This archetype not only restricts fathers' involvement in nurturing and caregiving but also devalues their potential to contribute in emotionally supportive ways.
Moving beyond this stereotype allows fathers to explore a full spectrum of parenting, from sharing in the joys and challenges of day-to-day child-rearing to being an active participant in household decisions and chores.
Embracing a more holistic view of fatherhood enables dads to forge stronger bonds with their children, offering them a model of gender inclusivity and emotional intelligence. Additionally, this shift can alleviate some of the pressures traditionally placed on mothers, promoting a more equitable sharing of parental duties. This reevaluation of the father's role challenges societal norms and encourages a family dynamic where both parents' contributions are acknowledged and valued, not simply for their economic worth but for their integral part in fostering a nurturing, supportive, and resilient family unit.
The Impact on Mothers and the Family Unit

When fathers actively engage in parenting and household responsibilities, the impact on mothers and the overall family unit is profound. Mothers, traditionally burdened with the lion's share of caregiving and domestic tasks, experience a significant alleviation of stress and an increased sense of partnership. This shared responsibility fosters a healthier work-life balance for both parents, reducing maternal burnout and enhancing family well-being. Moreover, it sets a powerful example for children, who learn the importance of equality, teamwork, and mutual support within the family.
By witnessing their fathers' active participation, children grow up with a more balanced view of gender roles, understanding that caregiving and emotional support are not solely women's responsibilities. This balanced approach to parenting leads to happier, more harmonious home environments, where all members feel valued and supported. The ripple effect of such dynamics encourages a culture of respect and collaboration, essential qualities for healthy, functional relationships both within and outside the family unit.
Breaking Down Gender Roles and Relationships
In today's society, the persistence of conventional gender roles continues to confine parents to outdated expectations that do not reflect the complexities of modern family life. By holding onto the belief that fathers should be the primary earners and mothers the chief caregivers, we limit the potential for a richer, more balanced familial interaction. This adherence to traditional roles not only hampers the emotional development and involvement of fathers but also unjustly burdens mothers with a disproportionate share of domestic and caregiving responsibilities. To foster a family dynamic that thrives on mutual respect, understanding, and shared duties, it is imperative to move beyond these archaic constructs.
Encouraging a departure from these norms enables families to model a dynamic of equality and shared responsibility, offering children a broader, more inclusive view of what it means to contribute to family life. In doing so, we not only challenge the status quo but also empower each family member to engage fully and authentically in their roles, free from the constraints of societal expectations. This shift towards a more egalitarian approach in parenting and household responsibilities is crucial for cultivating an environment where both parents can flourish in their individual and collective roles, demonstrating to children the value of collaboration, respect, and flexibility in family relationships and beyond.
The Myth of Masculinity and Parental Involvement

The prevailing notion that active fatherhood detracts from a man's masculinity is a significant impediment to balanced family involvement. This myth, deeply ingrained in societal norms, suggests that emotional availability and caregiving are at odds with traditional male characteristics. However, embracing these roles actually demonstrates profound strength and self-assurance. It is crucial to redefine masculinity to include the tenderness, empathy, and involvement in day-to-day family life that contribute to the holistic development of children. By challenging these outdated perceptions, fathers can reclaim their rightful place in the emotional and physical landscape of parenting.
This transformation not only benefits their relationships with their children but also models for future generations a more inclusive definition of what it means to be a man. Encouraging men to dismantle these barriers and engage fully in all aspects of parenting supports a family dynamic rich with diversity in care and interaction. The journey toward redefining masculinity to encompass the full spectrum of parental involvement is a vital step in fostering families where every member can thrive in an atmosphere of mutual respect and shared responsibilities.
The Benefits of Co-Parenting
Embracing co-parenting leads to a wealth of advantages that extend across the entire family unit. Children thrive under the care of both parents, gaining access to varied life lessons, emotional support, and a deeper sense of security. This dual involvement helps in the development of well-rounded individuals by exposing them to diverse problem-solving approaches, coping mechanisms, and nurturing styles. For parents, the shared responsibility lightens the individual burden, creating space for personal growth and stronger marital relationships.
The cooperative effort in parenting responsibilities fosters an environment of mutual respect and understanding, significantly reducing the potential for conflict and resentment. Such a dynamic promotes effective communication and teamwork, laying a solid foundation for children to learn valuable interpersonal skills. Furthermore, engaging in co-parenting allows for a more balanced lifestyle, where both parents can pursue their career ambitions while ensuring their family life remains a top priority. This approach not only enriches the parental experience but also models a healthy, collaborative, and supportive relationship for children, setting a precedent for their future relationships and parenting styles.
A Call to Action for Men and Women

The moment has arrived for a significant cultural shift in our understanding and appreciation of fatherhood within the context of family life. Both men and women must advocate for a more inclusive approach to parenting, highlighting the indispensable role fathers play in the emotional and developmental growth of their children. This endeavor requires a collective effort to dismantle the deep-seated stereotypes that limit paternal involvement to financial contributions. We need to foster an environment where fathers feel empowered and expected to engage deeply in the parenting process, from the tender moments of infancy to the complex challenges of adolescence.
Promoting the concept of co-parenting as a societal norm rather than an exception is essential. This includes encouraging workplaces to recognize and support the parenting roles of both fathers and mothers, thereby facilitating a more balanced distribution of domestic and professional responsibilities. Additionally, educational initiatives aimed at new and expecting parents can provide the tools and confidence needed for fathers to embrace their roles fully.
By uniting in this cause, we stand to benefit the fabric of our families, enhancing the well-being of all members and providing our children with a model of equality, cooperation, and respect. It’s about cultivating a generation that values emotional intelligence and mutual support, setting the stage for a future where the nurturing influence of both parents is not just welcomed, but expected. Let's commit to championing this change, for the betterment of our families and society at large.
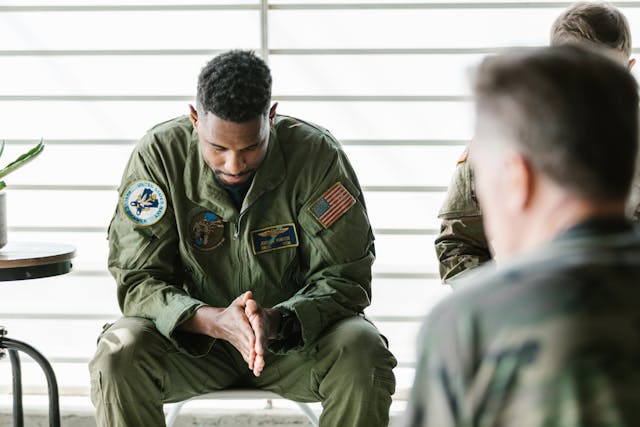

Experiencing or witnessing a profoundly distressing or threatening event can lead to the development of post-traumatic stress disorder, commonly known as PTSD. When you have PTSD, you get very anxious. Also, you have nightmares or relive the event that caused you to feel like that. Very often, it’s too much to take. To go through this, you might begin drinking. You might even try extremely dangerous substances just to be able to cope with your emotions. That is how you become dependent on substances. We will show you how PTSD and addiction are connected and how they make each other worse. When you understand this, you will make informed decisions, ask for professional help, and start living healthier lives.
What is PTSD?
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition. It is triggered when you experience or witness a traumatic event. Many signs of trauma can help you recognize this condition. You might get flashbacks of that event, see nightmares, or feel severely anxious. Also, you might have uncontrollable thoughts about it.
Some common triggers of PTSD are:
● Military combat
● Serious accidents, like car crashes
● Natural disasters, like floods or earthquakes
● Violent personal assaults, such as robbery or attack
● Abuse or domestic violence.
How PTSD affects daily life
It is not easy to live with PTSD. What happens is - you feel scared or nervous, even in safe situations. You tend to avoid places or people that bring back the memories connected to the trauma. Your sleep gets disrupted, as well. You can’t concentrate, and you feel angry and irritable. Much of the time, you feel sad.
Of course, having these feelings makes it hard to do everyday activities. For example, working, going to school, or even socializing is difficult. Unfortunately, your relationships suffer, as well.

What is addiction?
Addiction is a serious condition where you become unable to stop using a substance, even though it causes harm to your health, relationships, and daily responsibilities. You change your brain’s reward system when you use the substance repeatedly. That makes your brain dependent on the substance. You can become addicted to many different substances, such as:
● Alcohol,
● Prescription drugs like painkillers or sedatives,
● Illegal drugs like heroin, cocaine, or methamphetamine,
● Nicotine, found in cigarettes and vaping products.
How addiction starts and affects your life
Addiction starts with the repeated use of a substance. At first, you feel the effects of the substance strongly. Then, when you start using regularly, your body becomes tolerant. This tolerance means that you now need higher amounts of the substance to get the same feeling. The substance becomes a central part of your life as you consume more. This dependence on the substance can spiral into addiction.
Once addiction takes hold, it can disrupt various aspects of your life. Here are some of its effects:
- Health complications: Chronic use can lead to severe health issues such as heart, lung, and liver diseases.
- Relationship strain: Behavioral changes associated with addiction can damage your relationships with loved ones.
- Performance issues: Addiction can impair your focus and productivity, causing problems at work or school.
- Economic strain: The costs of sustaining an addiction can lead to financial hardship.
- Legal troubles: Efforts to acquire more substances can sometimes result in legal issues.
How PTSD and addiction are connected, and their impact
How do PTSD and addiction relate? Experiencing PTSD often entails grappling with overwhelming feelings of unease, tension, or profound melancholy. These emotions can become so overwhelming that you might feel trapped or powerless. Seeking solace, one might turn to substances like alcohol or drugs for temporary respite. This transient respite underscores the direct link between PTSD and addiction. For instance, if recurrent nightmares disrupt your sleep, indulging in alcohol may momentarily offer a sense of escape, aiding in relaxation and reducing feelings of overwhelm. Nevertheless, this respite is brief and can swiftly foster a dependency on such substances merely to restore a semblance of equilibrium.

Impact of PTSD and addiction on health
When you suffer from PTSD and addiction in combination, the risk of heart disease is higher. That happens because there are harmful effects of substances that go together with stress. Your liver gets damaged, too. It processes the substances you use, especially if you use a lot or very often. Furthermore, stress and using drugs and alcohol will weaken your immune system. That puts you in a bad position when your body needs to fight infections. Not only that, you get distracted from PTSD symptoms, and substances impair your judgment, which causes accidents and injuries.
There are mental health risks as well. After a very short period, when substance abuse reduces your PTSD symptoms, it starts making them even worse. You are more likely to become depressed. Also, substances affect your cognitive functions. You cannot think anymore, you forget important information, and you can’t make the right decisions.
Treatment options for PTSD and addiction
You need treatment from professionals who know how PTSD and addiction are connected. One important thing about treating PTSD and addiction is to treat them together. When only one condition is addressed, the other condition might continue to affect you. Some effective approaches are:
● Trauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT): This helps you identify and change negative thinking and behaviors. It can address both trauma responses and patterns of substance use.
● Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR): This therapy is specifically aimed at treating trauma and can be very helpful in processing and reducing the distress from traumatic memories.
● Group therapy: Participating in group sessions can provide support from peers who are dealing with similar issues, which can reduce feelings of isolation and shame.
Choosing the right treatment: The benefit of inpatient rehab facilities
For individuals grappling with the combined challenges of PTSD and substance addiction, the choice of treatment environment is important. Consequently, many New York residents opt for treatment in New Jersey, seeking the quieter, more focused, and often more affordable settings that facilities there can offer, away from the hustle and intense pace of their home state. By choosing a specialized inpatient rehab facility in New Jersey, NY locals can access tailored care that fosters recovery in a conducive environment. These centers offer a controlled environment that is crucial for those who are dealing with severe manifestations of PTSD and dependence on substances. These facilities' continuous access to medical and psychological assistance is indispensable during the initial recovery stages.
Choosing a rehab center in New Jersey, away from the familiar settings of NYC, can also provide strategic benefits. It helps individuals distance themselves from environments that may trigger their PTSD symptoms or substance use, thereby increasing the effectiveness of the recovery efforts. The proximity of New Jersey to New York facilitates family involvement in the recovery process, allowing for regular therapy participation and visits, which are essential components of successful rehabilitation.
Enrolling in an inpatient rehab center can profoundly impact an individual’s recovery trajectory. These centers are specifically prepared to manage the dual diagnosis of PTSD and addiction by implementing therapies designed to address both conditions comprehensively. This holistic approach is crucial as it targets the underlying and overt aspects of the disorders, laying a strong foundation for sustained recovery.
Social support will help you
A study approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) at the Medical University of South Carolina shows that you can benefit from social support. There is a greater decrease in the use of substances and PTSD symptoms during treatment when a person has strong social support. It can make treatment more effective.
Look for lasting solutions
We know that drinking and using drugs make you feel better when you cannot cope anymore. However, it is a quick fix. In the long run, it leads to more problems than you think it solves. You get addicted and create a cycle that makes your PTSD symptoms even worse than before. Now that you know how PTSD and addiction are connected, you ought to get help from healthcare experts who understand how PTSD and addiction are connected. They will guide you and help you explore your triggers and traumas, and eventually, you will better your relationships and improve your performance at work or school. You will get to live a more fulfilling and enjoyable life.