
Have you ever experienced the strong desire to forge your own path, only to hesitate for fear of losing your faith or alienating yourself from your community? Do you wrestle with doubts about the legitimacy of your emotions or find it challenging to rely on yourself? Perhaps you've also encountered situations where affection or gratitude felt strangely detached or unreachable. Such experiences are not uncommon for individuals grappling with the aftermath of religious trauma, where the path to self-discovery often feels fraught with conflict between personal growth and communal belonging.
Understanding Religious Trauma
Religious trauma is a deeply impactful form of emotional and psychological injury. It is trauma that arises from harmful experiences within a religious context. Individuals may suffer from religious trauma due to a variety of reasons. These may be exposure to toxic doctrines, manipulation, spiritual abuse, or the rejection by their faith community. This trauma often manifests as intense feelings of guilt, profound shame, or pervasive fear. A person can feel an enduring loss of trust in both oneself and in higher powers.
The damage inflicted by religious trauma can profoundly affect one’s emotional well-being. Its can lead to a disconnection from personal emotions and a pervasive sense of unworthiness. Such experiences challenge the core of an individual's identity and beliefs, creating inner turmoil and conflict that can persist without intervention. In some settings, the symptoms of religious trauma can be similar to those of complex post-traumatic stress disorder (C-PTSD).
An Introduction to Internal Family Systems (IFS)

Internal Family Systems (IFS) stands out as a revolutionary psychotherapeutic approach designed to foster self-awareness and healing. It has a wide range of applications that can be used in healing trauma. At its core, IFS posits that the mind is naturally segmented into multiple sub-personalities, or "parts." These parts each have their unique viewpoints, emotions, and memories. They often take on distinct roles within the psyche, such as protectors, managers, and exiles.
Each of these categories plays a pivotal role in our mental ecosystem. Protectors and managers work to shield the individual from pain and maintain daily function. Exiles carry burdens of trauma and pain. Both of these examples are frequently a result of adverse experiences such as religious trauma.
What sets IFS apart is its holistic focus on the individual's "Self," the essence of who they are beyond their parts. The Self is characterized by its innate capacity for compassion, clarity, courage, and connectedness. Through the IFS process, individuals are encouraged to assume a leadership role within their internal system, guiding their parts with kindness and understanding. This therapeutic journey involves identifying and addressing the parts that have been hurt or have taken on extreme roles due to religious trauma, thereby restoring balance and promoting psychological healing. By fostering an internal environment of empathy and acceptance, IFS enables individuals to embark on a path toward lasting recovery and self-discovery, transforming the way they relate to themselves and their past experiences.
How IFS Addresses Religious Trauma
In the context of healing from religious trauma, IFS offers a powerful and empathetic approach. It facilitates a deep connection with the wounded parts of the psyche that harbor the scars of religious abuse, neglect, or misunderstanding. Through IFS, individuals learn to approach these vulnerable aspects of themselves with the compassion and empathy they might have been denied in their religious experiences. By fostering an environment where no part is judged and every feeling is validated, the process enables the person to safely explore the impact of their trauma.
Importantly, IFS assists in distinguishing between one's faith and the harmful interpretations or applications of it that caused pain, allowing for a nuanced understanding of one's beliefs and values. This nuanced exploration encourages the reevaluation of beliefs in a way that honors one's inner truth and facilitates a healing reconnection with one’s spiritual self. As such, IFS does not seek to change one’s relationship with their faith directly but rather to heal the internal wounds inflicted by traumatic religious experiences. This approach empowers individuals to redefine their spiritual path on their own terms, leading to a more authentic and fulfilling spiritual life.
The Role of the Self in Healing

In the healing journey through IFS, the Self is instrumental, acting as an internal healing agent that navigates and integrates the various parts of an individual's psyche. This pivotal role involves leveraging the Self's inherent qualities of compassion, clarity, courage, and connectedness to embrace and soothe the parts that have been damaged or are carrying heavy burdens due to religious trauma.
The engagement of the Self allows for a unique therapeutic dialogue within the person, where wounded parts are heard, acknowledged, and understood without judgment.
Through this process, individuals discover an internal safe space where they can address their trauma directly, offering the wounded parts the empathy and acceptance they may have missed. This empowerment by the Self fosters a profound internal healing environment, promoting a reconciliation of conflicting internal elements and leading to a harmonious state of being. Engaging the Self in this manner not only facilitates the healing of religious trauma but also enhances the individual’s overall resilience, self-esteem, and emotional equilibrium.
Practical Steps to Begin Healing with IFS
Embarking on the healing journey with Internal Family Systems (IFS) in the wake of religious trauma requires a thoughtful approach. Your first step should be seeking out a qualified therapist skilled in IFS, with a strong background in addressing religious trauma. This professional can guide you through the nuanced process of getting acquainted with your internal parts, especially those carrying the weight of your trauma. They'll facilitate conversations that enable you to approach these parts with curiosity, compassion, and empathy.
Engaging in regular therapy sessions provides a structured environment where you can safely explore the depths of your experiences and begin the process of healing. Additionally, engaging in self-led IFS exercises, recommended by your therapist, can deepen your understanding and foster an ongoing dialogue with your internal family. Journaling about your thoughts, feelings, and discoveries after each session can also enhance your healing journey, providing clarity and insight into your progress. Embracing this path with patience and an open heart will gradually illuminate the way to reconciliation and peace within yourself, allowing you to redefine your spiritual beliefs and identity on your own terms.

Art therapy is a powerful tool that often goes unrecognized in the world of mental health treatment. This form of therapy utilizes the creative process of making art to improve a person's physical, mental, and emotional well-being. When traditional talk therapy fails to adequately address deep-seated trauma, art therapy steps in to provide a unique outlet for expression and healing. In this blog post, we will explore the role of art therapy in the context of Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) therapy, a widely-used approach for treating trauma and other psychological issues.
Understanding Art Therapy and Its Foundations
At its core, art therapy is built on the premise that engaging in the act of creating art is inherently therapeutic. It can foster personal growth, healing, and mental wellness. This therapeutic discipline offers a distinctive path for individuals to delve into their subconscious. Art enables them to uncover and address emotions and conflicts that might be challenging to express through words alone. It operates on the understanding that the creative process, as a form of nonverbal communication, has the unique capacity to reveal and work through complex emotional experiences.
\As participants navigate through various art-making techniques, they are provided with the opportunity to visualize their emotional landscape, guided by an Art Therapist. Hopefully, this may lead to profound insights and transformative healing experiences. This approach to therapy is especially beneficial for individuals who find conventional verbal communication limiting. Some people may feel it is even inadequate in expressing the depth of their internal experiences. Through art, they are able to articulate the inexpressible, facilitating a deeper connection with their own emotional realities, making it great for those struggling with words.
The Synergy Between Art Therapy and EMDR Therapy

The convergence of art therapy and EMDR creates a powerful alliance for tackling mental health issues like PTSD and anxiety, fitting different individual needs. This integrated approach facilitates a deeper engagement with the therapeutic process. It allows clients to unlock and process traumatic memories in a multifaceted manner.
While EMDR therapy focuses on desensitizing and reprocessing memories through bilateral stimulation, art therapy adds a layer of expressive richness. It provides a visual and tactile medium through which clients can explore and articulate their experiences.
The synergy of these therapies enhances emotional insight and healing. This is done by leveraging the strengths of each modality. EMDR's structured approach to trauma processing is complemented by the fluid and expansive nature of artistic expression. This combination broadens the avenues for understanding and healing, as well as caters to diverse needs and preferences, making therapy accessible to more individuals. By melding the cognitive with the creative, this integrated therapeutic approach opens up a dynamic space for healing, where emotions and memories can be navigated in a holistic and person-centered manner.
Art Therapy as a Safe Haven for Emotional Expression
Art therapy creates a nurturing and secure environment that enables individuals to delve into and express complex emotions with ease and without judgment. This method supports clients in accessing and articulating feelings that are otherwise hard to reach through more conventional therapeutic approaches. The process of making art in itself can be a profoundly healing act, offering a unique way to express emotions that might not be fully understood or verbalized. It invites an exploration of one's inner self, allowing for a non-verbal dialogue between the conscious and subconscious.
Through various artistic mediums, individuals can portray their emotions, experiences, and memories. Doing this fosters a sense of ownership and control over their healing journey. The tactile experience of handling art materials can also be soothing and grounding, providing a physical way to manage and express difficult emotions. In this respect, art therapy stands as a beacon of hope and solace for those navigating the complexities of healing from trauma. It can offer a path towards emotional clarity and relief that transcends the limitations of spoken language.
Enhancing the EMDR Process Through Art

Incorporating art therapy into EMDR therapy serves as a bridge to further facilitate the processing of traumatic memories. This integration allows individuals to symbolically represent their trauma, emotions, and recovery journey through art, offering a visual language for what might be too difficult to articulate with words. By engaging in artistic creation, clients can externalize their internal emotional struggles, making them more tangible and manageable.
This aids in the desensitization phase of EMDR and enriches the reprocessing phase. Clients can visually map out and reframe their experiences. The interplay between visual art and EMDR techniques fosters a comprehensive healing environment that honors both the cognitive and creative aspects of recovery. Through the use of art, individuals are empowered to navigate their healing process with a renewed sense of agency and creativity. It can potentially unlock deeper levels of emotional insight. This innovative approach underscores the adaptability and resilience of the human spirit. It offers a profound medium for transformation and growth within the context of trauma therapy.
Practical Approaches to Integrating Art Therapy with EMDR
To effectively weave art therapy into the framework of EMDR therapy, therapists can employ a variety of strategies tailored to enhance the therapeutic experience and foster deeper emotional healing. One practical approach involves inviting clients to engage in art-making activities directly before or after an EMDR session. This technique can serve as a powerful tool for clients to prepare mentally and emotionally for EMDR or to decompress and process their feelings afterward.
During EMDR sessions, therapists might also introduce art-based interventions. This is done as a means to facilitate the expression and processing of difficult emotions that arise. For instance, clients may be encouraged to draw or paint their emotional responses to EMDR prompts. Doing the art allows them to capture and explore their feelings in a tangible form. Additionally, art can be used to symbolize the transformation of negative beliefs into positive ones, helping clients visualize their journey towards healing in a concrete way.
Another approach includes utilizing art as a medium for clients to express their narrative or story. It provides a visual representation of their trauma and its impact on their life. This can be particularly useful in the reprocessing phases of EMDR, where understanding and reframing of past experiences is crucial.
By incorporating these practical art therapy techniques within EMDR sessions, therapists can offer a multi-layered healing experience that addresses the emotional and cognitive aspects of trauma, fostering a deeper, more holistic recovery process.

For many individuals in the LGBTQIA+ community, the journey of transitioning can be a tumultuous one. A journey filled with a range of emotions including anxiety and depression. The process of coming to terms with one's gender identity, undergoing hormone replacement therapy (HRT), and potentially having surgeries can be overwhelming. However, there is a therapeutic approach that may offer relief and help individuals feel more connected with their mind and body. It is called Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) therapy.
Understanding the Emotional Terrain of Transitioning
Transitioning, for many within the LGBTQIA+ community, represents not only a journey of physical metamorphosis but also of profound emotional exploration and self-discovery. This path, while ultimately affirming, is often fraught with complex feelings that can challenge even the strongest among us. As individuals embark on this deeply personal quest to align their outer selves with their inner truth, they may confront a myriad of societal pressures and internal conflicts that can exacerbate feelings of anxiety and depression.
The emotional landscape of transitioning is intricate and varied. It can encompass the excitement and hope of becoming more authentically oneself. It also comes with the fear and uncertainty that change inevitably brings. This anticipation of achieving congruence in one’s gender identity can be shadowed by the dread of potential isolation, misunderstanding, and discrimination. These external pressures compound the internal struggle, making it difficult for some to navigate the process of self-acceptance and self-love.

Complicating this journey further are the obstacles to finding affirming support and understanding. Misconceptions and stigma about what it means to transition can leave individuals feeling isolated and invalidated. This can intensify feelings of anxiety and depression. The daunting task of explaining one’s identity to others, fear of rejection, and the constant battle against societal norms and expectations can be overwhelming, leading to a profound sense of loneliness and despair.
As such, the emotional terrain of transitioning is marked by highs and lows. This can range from moments of exhilarating clarity as well as painful doubt. The process requires incredible resilience and courage, as individuals navigate through this complex emotional landscape in pursuit of their true selves. While the journey is inherently challenging, understanding and acknowledging these emotional experiences are crucial steps toward healing and growth.
An Introduction to EMDR Therapy
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) therapy emerges as a compelling psychotherapeutic approach. It is particularly renowned for its efficacy in addressing trauma-related conditions. EMDR facilitates the processing of distressing memories and emotional pain by activating both hemispheres of the brain through bilateral stimulation. This bilateral stimulation can be guided eye movements or tactile tapping. This innovative method aims to assist individuals in reorganizing and reinterpreting memories and emotions that are at the root of their psychological distress.
Developed in the late 1980s, EMDR has rapidly evolved and garnered empirical support as a treatment for various manifestations of psychological distress. Its unique methodology involves eight distinct phases, guiding clients from history-taking to the processing of traumatic events, and culminating in the consolidation of adaptive coping mechanisms. During EMDR sessions, therapists work closely with clients to identify specific distressing memories. They also help to identify negative beliefs about themselves that are associated with these memories. Through the structured phases of EMDR, clients are encouraged to focus on these memories while simultaneously engaging in bilateral stimulation. This dual focus facilitates the brain's natural healing process. This allows for the emotional charge of the memory to be diminished and for a more adaptive, empowering narrative to emerge.
Importantly, EMDR therapy goes beyond mere symptom relief, striving to foster a holistic sense of healing. Clients often report a decrease in distress related to specific memories and an overall improvement in their well-being. This gives room for an increased capacity to engage in their lives more fully. By directly targeting the underlying emotional impact of traumatic and distressing experiences, EMDR holds promise as a transformative therapeutic modality, especially for those contending with the profound emotional complexities associated with transitioning. Through its structured yet flexible approach, EMDR offers a pathway to healing that is both scientifically grounded and deeply attuned to the individual's psychological landscape.
EMDR in Action: Healing from Gender Dysphoria
EMDR therapy emerges as a vital resource for those grappling with gender dysphoria. Gender dysphoria is a condition characterized by profound discomfort due to a discrepancy between one’s experienced gender and the gender assigned at birth. This discomfort often manifests as severe anxiety, depression, and a disconnection from one’s body. In navigating these turbulent emotions, EMDR offers a promising avenue for healing and self-discovery.
Through its structured approach, EMDR targets the distressing memories and negative self-perceptions that underpin gender dysphoria. Individuals may harbor deep-seated beliefs of not belonging, being misunderstood, or feeling inherently flawed due to their gender identity struggles. EMDR engages the brain’s natural healing processes, allowing individuals to reprocess these painful experiences and beliefs. By focusing on specific memories or thoughts while receiving bilateral stimulation, clients can start to dissociate the negativity, shame, or fear attached to these memories. It can pave the way for more affirmative and empowering narratives about their gender identity.
The therapy’s unique ability to delve into the layers of emotional pain and cognitive dissonance that accompany gender dysphoria makes it an invaluable tool. It assists in alleviating the acute distress associated with living in a body that feels incongruent with one’s gender identity. As these individuals process their experiences through EMDR, they often find that the emotional charge of their distressing memories diminishes. This reduction in emotional intensity can lead to a significant decrease in anxiety and depression levels. It can ultimately contribute to a more harmonious internal experience.
As part of a comprehensive treatment plan, EMDR facilitates a journey towards self-acceptance and body congruence. It helps individuals in the LGBTQIA+ community to not only reconcile their past experiences with their gender identity but also fosters a stronger, more positive connection with their bodies and selves. Through EMDR, the path to healing from gender dysphoria becomes more accessible. It, empowers individuals to embrace their true identity with confidence and peace.
The Role of EMDR in Overcoming Anxiety and Depression
EMDR therapy stands out as a potent intervention for mitigating the profound impacts of anxiety and depression. This is particularly poignant for those undergoing the transition process. This therapeutic modality dives deep into the psyche, addressing the root causes of these mental health challenges. Through the distinctive mechanism of bilateral stimulation, EMDR aids individuals in accessing and processing the distressing memories and entrenched negative beliefs that fuel their emotional turmoil.
In the context of transitioning, anxiety and depression often stems from accumulated life experiences, societal rejection, or internalized stigma. Each of the forementioned can create a pervasive sense of being trapped or misunderstood. EMDR facilitates a re-examination and restructuring of these painful narratives, allowing for a transformative healing journey. By engaging the brain's innate capacity for resilience and recovery, it offers a path through which clients can gradually diminish the intensity of their emotional pain. It makes room for more adaptive, positive perspectives on their identities and experiences.

The therapy’s focused approach enables individuals to dismantle the complex layers of anxiety and depression. This helps to foster a sense of empowerment and renewed self-compassion. As these individuals progress through the phases of EMDR, they often report a significant alleviation of their symptoms. People begin to experience an enhanced ability to cope with stress and embrace their true selves with greater confidence.
EMDR's role in combating anxiety and depression is thus pivotal. It offers not just a means to cope but a route to thriving. Its application within the transitioning journey underscores a commitment to holistic well-being. Doing this, acknowledges the intrinsic link between resolving past traumas. It truly fosters a future where one's gender identity can be lived fully and authentically.
Finding Support and Embracing EMDR Therapy
In the pursuit of healing and self-discovery during transitioning, the role of supportive therapy cannot be overstated. It is critical to connect with therapists who possess a deep understanding of gender diversity. It is just as important that they exhibit a genuine commitment to creating a respectful and welcoming therapeutic environment. EMDR therapy has the profound potential to address the psychological distress associated with transitioning. This requires navigating with a therapist is skilled in its application and sensitive to the nuances of the LGBTQIA+ experience.
Choosing the right therapist involves seeking out professionals who are conversant with EMDR and actively affirm and celebrate LGBTQIA+ identities. Such therapists are instrumental in fostering a space where individuals can explore their feelings and experiences without fear of judgment or misunderstanding. They play a crucial role in facilitating the therapeutic process, guiding individuals through the nuanced phases of EMDR with empathy and understanding.
Embarking on EMDR therapy with a supportive therapist opens up avenues for profound emotional healing and growth. This therapy is done in a manner that is both empowering and transformative. It enables individuals to work through the layers of anxiety, depression, and trauma that transitioning can unearth. The journey with EMDR therapy is one of reclamation, allowing individuals to rewrite their narratives with strength and authenticity.
The decision to seek out EMDR therapy, paired with the support of a knowledgeable and affirming therapist, marks a significant step towards achieving psychological well-being and a deeper alignment with one’s true self. It underscores the importance of supportive relationships in the healing journey, reminding individuals that they do not have to navigate this path alone.

Trauma is a powerful force that can shape our behaviors, thoughts, and emotions in profound ways. For many individuals, past experiences of trauma can manifest in various parts of their psyche. This can influence how they interact with the world around them. Internal Family Systems Therapy (IFS) offers a unique approach to understanding and addressing these internal parts, helping individuals navigate their inner world with compassion and curiosity. By delving into the core concepts of IFS, we can uncover the transformative power of recognizing and integrating these parts for holistic healing and self-acceptance.
Unpacking the Core Concepts of Internal Family Systems Therapy
Internal Family Systems Therapy (IFS) introduces a compelling framework for understanding the mind's landscape. At its core, IFS posits that the psyche is composed of multiple sub-personalities, or "parts." These parts each have their distinct roles, perspectives, and attributes. They, but are not limited to, protectors, managers, and exiles. Protectors are often tasked with shielding the individual from pain and vulnerability. Managers attempt to control behavior and external relationships to avoid hurt or disappointment. Exiles carry the emotional burdens and traumas that the system has deemed too overwhelming or dangerous to confront directly.

The interaction between these parts can significantly influence an individual's behavior, emotional responses, and patterns of thinking. In navigating through the IFS process, individuals learn to identify and understand the specific roles these parts play. They learn how the parts contribute to complex coping mechanisms forged in response to trauma and stress.
A pivotal aspect of IFS is fostering a non-judgmental curiosity about these parts. This leads to a deeper understanding of their intentions, fears, and desires. This empathetic inquiry enables individuals to form a compassionate connection with their parts, rather than engaging in internal conflict or attempting to banish these aspects of themselves. The ultimate aim is to harmonize the internal system, allowing the individual's true Self—a concept referring to the person's core essence characterized by qualities such as calmness, curiosity, compassion, and confidence—to lead and bring about healing and equilibrium.
Through IFS, individuals embark on a transformative journey. This can cultivate a relationship with their inner parts that is rooted in understanding, acceptance, and healing. This therapeutic exploration encourages the integration of all parts, facilitating a path toward greater self-awareness and emotional well-being.
The Significance of Recognizing Internal Parts

Acknowledging the multitude of parts within our internal system unveils a rich tapestry of emotions, motivations, and desires. This drives our behavior and shape our reactions to the world around us. This intricate exploration into our inner selves is fundamental in the journey toward self-awareness and emotional maturity. By inviting each part to communicate its story, fears, and aspirations, we unlock a deeper dimension of understanding that transcends surface-level interactions with our psyche. This empathic engagement with our parts encourages a transformation from within. It is where the once fragmented aspects of our identity begin to coalesce into a more unified and harmonious whole.
Recognizing these internal parts also demystifies the reasons behind certain behaviors or emotional responses that may have previously seemed irrational or unfounded. It offers a clarifying lens through which we can view our actions, revealing the protective or defensive roles these parts play. This revelation not only fosters a climate of self-compassion but also equips us with the knowledge to navigate our internal world more effectively. We learn to approach each part with curiosity and kindness, valuing their presence as integral to our holistic well-being. This process, though nuanced and layered, is instrumental in cultivating a balanced and authentic self-relationship. It lays the groundwork for profound personal growth and healing.
Addressing Trauma Through the Lens of IFS

When we approach trauma through the insightful perspective of Internal Family Systems Therapy, we unlock a profound avenue for understanding and healing. Trauma, by its nature, disrupts our internal equilibrium, often leaving parts of us in distress. IFS provides a structured yet flexible framework for engaging with these parts, many of which harbor the pain and fear from traumatic experiences. Through the IFS model, individuals learn to identify and interact with these parts—be it protectors who work tirelessly to shield us from further harm, or exiles carrying the weight of our pain.
This therapeutic process involves gently uncovering the stories and burdens these parts hold, acknowledging their presence, and validating their experiences. It's through this compassionate acknowledgment that individuals can begin to ease the grip of trauma. The parts that were once isolated or in conflict can be understood and honored for their roles. This allows for a reorganization of the internal system that promotes healing and resilience.
In the safety of the therapeutic relationship, individuals are guided to lead with their Self. The Self being the core of calmness and clarity within. This self-leadership is pivotal in fostering a nurturing internal environment where parts feel seen and heard. This reduces their need to engage in extreme roles or behaviors. By reestablishing trust within the internal system, trauma's hold can be loosened. It can pave the way for resilience and a renewed sense of wholeness. Through IFS, healing from trauma transcends mere coping, evolving into a journey of self-discovery and empowerment.
The Role of Self-Leadership in Healing and Transformation

At the foundation of Internal Family Systems Therapy is the empowering principle of self-leadership. This concept emphasizes the significance of steering one’s inner world through the strength and guidance of the Self. It embodies the essence of compassion, clarity, and calmness. Cultivating self-leadership is vital for individuals seeking to heal and transform their lives. It can foster an environment where the internal parts can find harmony and peace under the direction of the true Self. This journey of self-leadership encourages individuals to embrace their ability to guide and support their parts with understanding empathy. This leads to profound shifts in how they relate to themselves and navigate their emotional landscapes.
In the process of engaging with and leading one's parts, an individual discovers the capacity to face life’s adversities with a newfound resilience and insight. This approach not only alleviates the distress of the parts but also promotes an internal alignment that propels the individual toward positive change and personal evolution. The practice of self-leadership is a transformative endeavor that positions the Self to be the beacon of hope and healing. It guides the individual through the complexities of their internal world and toward a path of self-discovery and enduring growth. Emphasizing the role of the Self in this capacity underlines the transformative power of leading from a place of inner strength and authenticity, essential for achieving a state of balance and well-being.
Real-Life Applications of IFS in Addressing Repetitive Patterns

Exploring the practicality of Internal Family Systems Therapy reveals its efficacy in unraveling and transforming deeply entrenched behavioral patterns. Individuals often find themselves caught in a loop of repetitive actions and responses that seem resistant to change. These patterns, whether manifesting as procrastination, aggression, or withdrawal, have roots in parts that developed strategies to protect the self from harm or emotional pain.
Through the lens of IFS, individuals gain insights into the origin stories of these parts. They start to understand their protective intentions and the contexts in which they were formed.
The process begins with identifying the parts involved in these patterns. This includes, acknowledging their efforts to protect, and exploring the historical trauma or experiences that led to the adoption of such strategies. This awareness creates a platform for compassion and empathy towards oneself, facilitating a dialogue between the Self and its parts. Techniques such as direct access, where individuals communicate internally with their parts, and unblending, the separation of the Self from its parts to reduce overwhelming emotions, are instrumental in this process.
As individuals learn to lead with the Self, they can negotiate new roles for their parts. They can begin to move away from destructive patterns. This can enable them to move towards behaviors that are in alignment with their true values and goals. This shift does not happen overnight but is a gradual process. The process is of healing and reorganization within the internal family system. It ultimately leads to more adaptive and fulfilling ways of being in the world.
Embracing Self-Acceptance and Integration for a Fulfilling Life

The essence of Internal Family Systems Therapy lies in its capacity to facilitate a profound embrace of every facet of one's being. As individuals journey through the process of identifying and engaging with their varied internal parts, a transformative shift toward self-acceptance begins to unfold. This path of integration is marked by an intentional and compassionate acknowledgment of each part's existence and its contribution to the individual's life narrative.
The realization that these parts, regardless of their roles, are fundamentally aimed at self-preservation and protection. It allows for a softening of internal resistance and a welcoming of all aspects of the self. Such a holistic embrace fosters a deep sense of completeness and unity within. It sets the stage for living in alignment with one's authentic self. As this internal harmony is achieved, individuals find themselves better equipped to face life's challenges with a resilient and grounded presence. This leads to a life that is not just endured but richly experienced and enjoyed.

Experiencing or witnessing a profoundly distressing or threatening event can lead to the development of post-traumatic stress disorder, commonly known as PTSD. When you have PTSD, you get very anxious. Also, you have nightmares or relive the event that caused you to feel like that. Very often, it’s too much to take. To go through this, you might begin drinking. You might even try extremely dangerous substances just to be able to cope with your emotions. That is how you become dependent on substances. We will show you how PTSD and addiction are connected and how they make each other worse. When you understand this, you will make informed decisions, ask for professional help, and start living healthier lives.
What is PTSD?
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition. It is triggered when you experience or witness a traumatic event. Many signs of trauma can help you recognize this condition. You might get flashbacks of that event, see nightmares, or feel severely anxious. Also, you might have uncontrollable thoughts about it.
Some common triggers of PTSD are:
● Military combat
● Serious accidents, like car crashes
● Natural disasters, like floods or earthquakes
● Violent personal assaults, such as robbery or attack
● Abuse or domestic violence.
How PTSD affects daily life
It is not easy to live with PTSD. What happens is - you feel scared or nervous, even in safe situations. You tend to avoid places or people that bring back the memories connected to the trauma. Your sleep gets disrupted, as well. You can’t concentrate, and you feel angry and irritable. Much of the time, you feel sad.
Of course, having these feelings makes it hard to do everyday activities. For example, working, going to school, or even socializing is difficult. Unfortunately, your relationships suffer, as well.

What is addiction?
Addiction is a serious condition where you become unable to stop using a substance, even though it causes harm to your health, relationships, and daily responsibilities. You change your brain’s reward system when you use the substance repeatedly. That makes your brain dependent on the substance. You can become addicted to many different substances, such as:
● Alcohol,
● Prescription drugs like painkillers or sedatives,
● Illegal drugs like heroin, cocaine, or methamphetamine,
● Nicotine, found in cigarettes and vaping products.
How addiction starts and affects your life
Addiction starts with the repeated use of a substance. At first, you feel the effects of the substance strongly. Then, when you start using regularly, your body becomes tolerant. This tolerance means that you now need higher amounts of the substance to get the same feeling. The substance becomes a central part of your life as you consume more. This dependence on the substance can spiral into addiction.
Once addiction takes hold, it can disrupt various aspects of your life. Here are some of its effects:
- Health complications: Chronic use can lead to severe health issues such as heart, lung, and liver diseases.
- Relationship strain: Behavioral changes associated with addiction can damage your relationships with loved ones.
- Performance issues: Addiction can impair your focus and productivity, causing problems at work or school.
- Economic strain: The costs of sustaining an addiction can lead to financial hardship.
- Legal troubles: Efforts to acquire more substances can sometimes result in legal issues.
How PTSD and addiction are connected, and their impact
How do PTSD and addiction relate? Experiencing PTSD often entails grappling with overwhelming feelings of unease, tension, or profound melancholy. These emotions can become so overwhelming that you might feel trapped or powerless. Seeking solace, one might turn to substances like alcohol or drugs for temporary respite. This transient respite underscores the direct link between PTSD and addiction. For instance, if recurrent nightmares disrupt your sleep, indulging in alcohol may momentarily offer a sense of escape, aiding in relaxation and reducing feelings of overwhelm. Nevertheless, this respite is brief and can swiftly foster a dependency on such substances merely to restore a semblance of equilibrium.
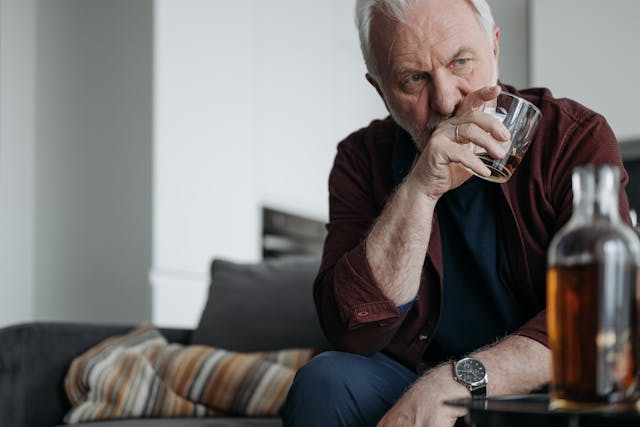

Impact of PTSD and addiction on health
When you suffer from PTSD and addiction in combination, the risk of heart disease is higher. That happens because there are harmful effects of substances that go together with stress. Your liver gets damaged, too. It processes the substances you use, especially if you use a lot or very often. Furthermore, stress and using drugs and alcohol will weaken your immune system. That puts you in a bad position when your body needs to fight infections. Not only that, you get distracted from PTSD symptoms, and substances impair your judgment, which causes accidents and injuries.
There are mental health risks as well. After a very short period, when substance abuse reduces your PTSD symptoms, it starts making them even worse. You are more likely to become depressed. Also, substances affect your cognitive functions. You cannot think anymore, you forget important information, and you can’t make the right decisions.
Treatment options for PTSD and addiction
You need treatment from professionals who know how PTSD and addiction are connected. One important thing about treating PTSD and addiction is to treat them together. When only one condition is addressed, the other condition might continue to affect you. Some effective approaches are:
● Trauma-focused cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT): This helps you identify and change negative thinking and behaviors. It can address both trauma responses and patterns of substance use.
● Eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR): This therapy is specifically aimed at treating trauma and can be very helpful in processing and reducing the distress from traumatic memories.
● Group therapy: Participating in group sessions can provide support from peers who are dealing with similar issues, which can reduce feelings of isolation and shame.
Choosing the right treatment: The benefit of inpatient rehab facilities
For individuals grappling with the combined challenges of PTSD and substance addiction, the choice of treatment environment is important. Consequently, many New York residents opt for treatment in New Jersey, seeking the quieter, more focused, and often more affordable settings that facilities there can offer, away from the hustle and intense pace of their home state. By choosing a specialized inpatient rehab facility in New Jersey, NY locals can access tailored care that fosters recovery in a conducive environment. These centers offer a controlled environment that is crucial for those who are dealing with severe manifestations of PTSD and dependence on substances. These facilities' continuous access to medical and psychological assistance is indispensable during the initial recovery stages.
Choosing a rehab center in New Jersey, away from the familiar settings of NYC, can also provide strategic benefits. It helps individuals distance themselves from environments that may trigger their PTSD symptoms or substance use, thereby increasing the effectiveness of the recovery efforts. The proximity of New Jersey to New York facilitates family involvement in the recovery process, allowing for regular therapy participation and visits, which are essential components of successful rehabilitation.
Enrolling in an inpatient rehab center can profoundly impact an individual’s recovery trajectory. These centers are specifically prepared to manage the dual diagnosis of PTSD and addiction by implementing therapies designed to address both conditions comprehensively. This holistic approach is crucial as it targets the underlying and overt aspects of the disorders, laying a strong foundation for sustained recovery.
Social support will help you
A study approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) at the Medical University of South Carolina shows that you can benefit from social support. There is a greater decrease in the use of substances and PTSD symptoms during treatment when a person has strong social support. It can make treatment more effective.
Look for lasting solutions
We know that drinking and using drugs make you feel better when you cannot cope anymore. However, it is a quick fix. In the long run, it leads to more problems than you think it solves. You get addicted and create a cycle that makes your PTSD symptoms even worse than before. Now that you know how PTSD and addiction are connected, you ought to get help from healthcare experts who understand how PTSD and addiction are connected. They will guide you and help you explore your triggers and traumas, and eventually, you will better your relationships and improve your performance at work or school. You will get to live a more fulfilling and enjoyable life.

Borderline personality disorder (BPD) is a mental health condition that can be challenging for both the individual experiencing it and their loved ones. When it comes to teenagers exhibiting symptoms of BPD, it can be especially difficult for parents to know how to best support their child. In this blog post, we will discuss how to recognize BPD symptoms in teenagers, how to support your child with empathy and understanding, when to seek professional help, available treatments for teenagers with BPD symptoms, the role of Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT), and whether Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) can help with BPD symptoms.
Recognizing BPD Symptoms in Teenagers
Identifying borderline personality disorder in adolescents involves observing various behavioral and emotional signs that deviate significantly from the expected developmental trajectory for their age group. These teenagers often experience profound emotional instability, marked by intense, rapidly fluctuating moods that can last from a few hours to a few days. Their relationships may be characterized by a pattern of idealization and devaluation, swinging between extreme closeness and equally intense dislike or anger towards friends and family. Impulsivity is another hallmark, manifesting in risky behaviors such as substance abuse, reckless driving, or binge eating.
A pervasive fear of abandonment might lead them to go to great lengths to avoid real or imagined separation or rejection. Self-harm behaviors, including cutting or burning, and recurrent thoughts of suicide can also be indicative of BPD. Additionally, these teens might have a significantly distorted self-image, struggling with identity issues, and often seeing themselves as fundamentally bad or unworthy. It's also not uncommon for them to feel chronically empty, unable to gain a sense of fulfillment from their usual activities. Recognizing these symptoms as potential indicators of borderline personality disorder is the first step toward seeking the help and support these teenagers need to navigate their complex emotional landscape.
Supporting Your Child with Empathy and Understanding

Navigating the complexities of borderline personality disorder in teenagers requires a foundation of empathy and understanding from parents. This empathetic approach involves actively listening to your child’s experiences without rushing to judgment or immediate solutions. Acknowledge the realness and depth of their feelings, showing that you see and accept their emotional state.
This validation is a critical step in building trust and can significantly ease their emotional turmoil. It's also beneficial to create an environment that encourages open communication, allowing your child to share their thoughts and feelings without fear of criticism or dismissal.
By demonstrating that their feelings are valid and important, you encourage self-expression and provide a vital outlet for their emotions. Remember, your response to their expressions of pain or frustration can either reinforce their sense of security and self-worth or exacerbate their emotional struggles. Consequently, engaging in calm, non-reactive conversations, even when the content may be challenging, is crucial. In doing so, you not only support their emotional needs but also model healthy communication and coping strategies. Encouragingly, this supportive approach does not necessitate perfect execution; the effort to understand and the willingness to learn and adjust are themselves powerful demonstrations of love and support.
Knowing When to Seek Professional Help

Recognizing the signs that it's time to seek professional assistance is a critical step for parents navigating the waters of borderline personality disorder with their teenager. When symptoms persistently interfere with your child's daily functioning—impacting their academic performance, social interactions, or family life—it's a clear indication that additional support is needed.
Other red flags include escalating self-harm behaviors, expressions of suicidal ideation, or an inability to manage intense emotional episodes despite your best efforts to provide support at home.
Consulting with a mental health professional can offer a pathway to diagnosis and tailored treatment options. They bring a level of expertise and an outside perspective that can be invaluable in understanding your child’s needs and determining the most appropriate interventions. Engaging with professionals early can also pave the way for a more positive prognosis. Equipping your teenager with coping mechanisms and strategies to navigate their emotions effectively is the goal. Remember, reaching out for help is a sign of strength. It is also an important step in supporting your teenager’s mental health and overall well-being.
Exploring Treatment Options for BPD

For teenagers grappling with borderline personality disorder symptoms, a multifaceted treatment approach is often most beneficial. This can encompass individual psychotherapy, which provides a safe space for teens to explore their thoughts and feelings, alongside group therapy sessions that help develop social skills and offer peer support. A key component of effective treatment is skills training. This focuses on building the coping mechanisms necessary for emotional regulation and distress tolerance.
Medication may also play a role in managing specific symptoms of BPD. These symptoms can be mood swings or depression, although it is not a standalone solution. It's crucial to consult with a psychiatrist who has experience with adolescent mental health. It is important to carefully assess the need for medication and to monitor its effectiveness and any side effects closely.
Family therapy is another vital aspect of treatment, aiming to improve communication and reduce familial stress. It provides parents and siblings with the tools to support the teen effectively, fostering a home environment conducive to healing and growth.
Engaging in a comprehensive treatment plan, tailored to the individual needs of the teenager, can significantly enhance their ability to navigate the challenges of BPD. Collaborating with mental health professionals to continuously assess and adjust this plan ensures that it remains aligned with the evolving needs of the teenager as they progress through therapy.
The Role of Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) stands out as a cornerstone in the therapeutic landscape for managing borderline personality disorder. Designed explicitly with the complexities of BPD in mind, DBT integrates a unique blend of cognitive-behavioral techniques with the concept of mindfulness, drawn from Eastern meditative practices. This therapy is structured around four primary modules: mindfulness, distress tolerance, emotion regulation, and interpersonal effectiveness. Each module targets specific aspects of BPD. This offers teenagers practical skills to deal with the emotional dysregulation and turbulent relationships that often characterize this condition.
Mindfulness practices encourage an increased awareness of the present moment. It helps individuals to observe and accept their thoughts and feelings without judgment. Distress tolerance skills are vital for navigating intense emotional episodes. Thus teaching teens how to survive crisis situations without resorting to self-destructive behaviors. Emotion regulation tools help in identifying and managing overwhelming emotions, while interpersonal effectiveness techniques focus on fostering healthier and more stable relationships. Through a combination of individual therapy sessions and group skills training, DBT empowers teenagers to take control of their BPD symptoms, fostering a path towards healing and personal growth.
Can EMDR Help with BPD Symptoms?
EMDR has been primarily recognized for its effectiveness in treating post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). However, its utility in managing symptoms associated with borderline personality disorder is gaining attention. Given the high prevalence of traumatic experiences in the histories of individuals with BPD, EMDR offers a promising avenue for addressing these underlying issues. This therapeutic technique focuses on desensitizing the individual to the emotional impact of traumatic memories. This is done through guided eye movements, thereby diminishing the distress these memories can cause.
For teenagers with BPD who have experienced trauma, EMDR can complement existing treatments. This can be done by helping to process these traumas more effectively. This can, in turn, reduce some of the emotional intensity and impulsivity that complicate BPD. However, it's crucial to approach EMDR as part of a broader, comprehensive treatment strategy. It should be tailored to the teenager's specific needs and symptoms. Engaging a qualified therapist who can assess the suitability of EMDR in the context of the teenager's overall treatment plan is essential.
Taking Care of Yourself as a Parent
Navigating the complexities of caring for a teenager with borderline personality disorder symptoms demands a significant emotional investment. At times, it can leave parents feeling overwhelmed and exhausted. It's essential to acknowledge that your well-being is just as crucial as that of your child. Engaging in self-care practices is not a luxury but a necessity. It enables you to maintain the resilience and emotional capacity required to offer sustained support. Finding avenues for your own support can make a profound difference in your ability to cope with the challenges that come with parenting a child with BPD.

Consider exploring support groups specifically tailored for parents dealing with similar situations. These groups provide a valuable space for sharing experiences, receiving advice, and gaining comfort from the knowledge that you are not alone in your journey. Additionally, integrating mindfulness and relaxation techniques into your daily routine can help manage stress and replenish your emotional resources. These practices can range from meditation and yoga to simply spending time in nature or engaging in hobbies that bring you joy.
It's also important to establish healthy boundaries to safeguard your emotional and physical well-being. Recognize and respect your limits, understanding that taking time for yourself is not an act of selfishness. It is a vital component of providing effective support for your teenager. Remember, seeking professional guidance for yourself, whether through therapy or counseling, can provide additional strategies for managing stress. This ensures that you are in the best possible position to care for your child. Prioritizing your health and well-being is a cornerstone of being a supportive and effective parent in the face of BPD's challenges.

Do you often find yourself feeling hollow, as if something within you is missing? This unexplainable feeling of emptiness could be more than just a passing phase of ennui. It might be linked to a less-talked-about yet prevalent form of childhood trauma - emotional neglect.
Understanding Childhood Emotional Neglect
Childhood emotional neglect is an insidious form of child abuse that often flies under the radar. Unlike physical neglect or abuse, it doesn't leave visible scars or bruises, making it less conspicuous and frequently disregarded. It can be defined as a failure by caregivers to provide the emotional support and attention that children need to flourish and grow.
This neglect might not be intentional; parents might dismiss, ignore, or trivialize their child's emotions due to their lack of understanding or their own unmet emotional needs. Regardless of the reason, this neglect leaves a lasting impression on the child. It's akin to an unseen emotional void that the child carries forward into their adult life, often manifesting as a pervasive feeling of emptiness.
The impact of this neglect can be profound and far-reaching, affecting the child's ability to form healthy emotional connections and often resulting in feelings of inadequacy, unlovability, or a sense of being fundamentally flawed. Recognizing this form of neglect is the first step towards understanding the emptiness you might be feeling.
The Invisible Scars of Emotional Neglect

Emotional neglect etches deep, unseen imprints on a child's emotional fabric. Our emotional needs in childhood are equally important as our physical ones. They help us construct a healthy sense of self-worth. When these needs are consistently unfulfilled, it can disrupt our emotional development. This disruption often translates into a lingering feeling of being unwanted, insufficient, or inherently flawed.
These invisible scars have a profound influence on the child's self-esteem and perception of self-worth, subtly shaping their personality and their perspective of the world. Though invisible to the naked eye, these scars run deep, influencing every interaction and relationship in their adult life. So, while these wounds may not be visible, their impact is seen and felt in various aspects of the individual's life, often appearing as the unshakeable feeling of emptiness we're discussing here.
The Connection Between Emotional Neglect and Feeling Empty
The lingering sense of emptiness you experience as an adult may be deeply rooted in the emotional neglect you experienced during your childhood years. This persistent emptiness typically stems from not having our emotional needs adequately addressed during critical developmental stages, creating an emotional deficit. Such neglect may lead to difficulty in forging a strong emotional connection with oneself and others, resulting in a pervasive feeling of emptiness. You might feel like you're observing life from the outside looking in, or find yourself often feeling emotionally detached, and struggling to find pleasure or purpose in day-to-day experiences. This internal void, although invisible and often misunderstood, is a significant indicator of unmet emotional needs from childhood, manifesting itself in your adult life. This connection between childhood emotional neglect and the ongoing feeling of emptiness is a critical piece in understanding and addressing the root cause of such distressing emotions.
Signs You Might Have Experienced Childhood Emotional Neglect
Recognizing emotional neglect can be tricky because it’s often about the absence of emotional support and care rather than outright harm. But, there are several indicators you can look for. You may have a hard time identifying or verbalizing your emotions. Do you often feel like you don't fit in or belong, no matter where you are? If you’re overly sensitive to rejection or criticism, this could be a sign.
You might also find yourself with a powerful fear of dependency, finding it hard to rely on others for help or support. You could be wrestling with self-discipline issues or have a penchant for perfectionism. These are all signs that may hint at past emotional neglect. Keep in mind, these signs are not definitive proof but potential markers. If you find yourself identifying with a lot of these signs, it might be beneficial to reach out to a mental health professional for a deeper exploration of your feelings and experiences.
Healing from Childhood Emotional Neglect
The path to recovery from childhood emotional neglect is a voyage of self-understanding and self-love. It commences with acknowledging and coming to terms with your past experiences. The subsequent stage involves cultivating an intimate bond with your own feelings and requirements. This could entail seeking professional guidance, delving into mindfulness practices, cataloging your emotions through journaling, or cultivating habits of self-care. Unraveling the emotional neglect of the past isn't a journey you have to embark on alone. Therapists who specialize in this area can provide invaluable guidance and support.
Self-Care and Emotional Nurturing
One of the most essential components on your journey to healing from childhood emotional neglect is practicing self-care. This goes beyond maintaining your physical well-being with regular exercise and nutritious meals. Yes, taking care of your physical health is vital, but healing from emotional neglect necessitates nurturing your emotional health, as well. Establish and enforce healthy boundaries in relationships to safeguard your emotional space. Cultivate a practice of self-compassion. Be patient with yourself, offering the same grace and kindness you would to a dear friend.
Find joy and comfort in activities that resonate with you, that make your heart sing and your soul feel at peace. Making your emotional well-being a priority isn't selfish; it's necessary. You've spent a lifetime carrying the weight of emotional neglect, it's high time to put it down and nourish your emotional health. Remember, self-care isn't indulgence, it's fundamental to your healing process. Be gentle with yourself. You are worthy of love, care, and kindness.
Reach Out - You're Not Alone
Recognizing that hollow feeling inside you as a sign of childhood emotional neglect is the first crucial step towards healing. Now, the journey towards recovery begins. Remember, you don't have to traverse this path alone. Confide in loved ones, share your experiences, and allow them to offer you support and encouragement. Consider joining a support group; engaging with others who have had similar experiences can be incredibly affirming and healing.
If you're comfortable, seek help from mental health professionals specializing in childhood trauma. They can provide you with effective strategies and techniques to help you understand and overcome the impact of emotional neglect. Reaching out may feel daunting, but the rewards are tremendous. The path to recovery may be long, but you'll find strength, resilience, and healing along the way. You've been carrying the burden of emotional neglect long enough, it's time to lighten the load. Let people in, let them help, and remember, you are deserving of love and care.

As parents, it's often our first instinct to shield our children from failure. We support them, help them, and often extend our helping hand with their homework to ensure their success. However, the question arises: When is it appropriate to let your children fail? At what age can you stop helping them with homework before it becomes a battle each time? Is it our own insecurities that make us hard on our children? In today's blog post, we'll delve into these delicate issues and explore how the therapy method EMDR can be beneficial in this situation.
The Value of Allowing Children to Fail
Navigating the tumultuous waters of parenthood, it can be heart-wrenching to witness our children grapple with failure. Yet, it's crucial to remember that these moments of defeat are stepping stones on the path to self-improvement and resilience. By experiencing failure, children learn the invaluable art of problem-solving, fortify their resilience, and cultivate a positive attitude towards overcoming obstacles.
While it might feel instinctual to swoop in and save the day during homework crises, doing so can inadvertently strip them of these crucial life-building opportunities. Our intent is not to advocate for a hands-off approach that borders on neglect. Instead, the focus should be on fostering an environment where children feel secure enough to stumble, pick themselves up, learn from their blunders, and move forward with newfound wisdom and self-confidence.
On this journey, it is not the fall that shapes the child but their capacity to rise each time they stumble. As parents, our role morphs from fixers of problems to cheerleaders of resilience, applauding their determination, and celebrating their growth, one homework assignment at a time. As a result, allowing children to experience failure is not a sign of deficient parenting; it's a testament to our commitment to raising individuals who can bravely face challenges and come out stronger.
Finding the Right Balance in Homework Help

Navigating the homework waters can be a tricky task. It's a part of parenting, a normal routine, but knowing when to reel in the rescue rope can be a bit complex. As children progress through their educational journey, they need to build a sense of self-reliance. Our role gradually needs to transition from homework helper to a facilitator who empowers independent thinking.
This doesn't mean stepping away completely and leaving them in the lurch. You can't just stop helping with homework cold turkey. It's more about fostering an atmosphere of independence, promoting their self-confidence, and honing their problem-solving abilities. For instance, instead of providing outright answers, nudge them towards finding their own solutions. Give them the tools to critically think, explore, and discover. Guide them with constructive questioning or provide directional support without giving away the answers.
Gradually reducing the extent of help provided is also an effective strategy to keep homework from turning into a battleground. This encourages children to take up more accountability for their education, teaching them the crucial skill of responsibility. Eventually, they may feel confident enough for you to stop helping them with their homework!
Remember, this is a journey, not a race. Mistakes will be made, and tasks might take longer to be accomplished. But each step your child takes independently is a significant stride towards confidence, resilience, and problem-solving mastery. This journey will not only prepare them for academic success but equip them for the challenges that life will undoubtedly throw their way.
Uncovering Parental Insecurities

Uncovering parental insecurities is not only critical for the overall emotional health of parents, but it can significantly affect the upbringing of their children. If unaddressed, these insecurities can contribute to parenting styles imbued with high levels of control or anxiety symptoms. Thus, to break this cycle, therapies such as EMDR and counseling for teens, can be beneficial in addressing these insecurities, modifying anxiety symptoms, and promoting healthier parenting styles. In particular, EMDR therapy can help parents reprocess traumatic memories that may fuel their insecurities, whereas counseling for teens may assist in alleviating anxiety symptoms caused by parent-child dynamics. With improved parental awareness and more proactive anxiety treatment, healthier parenting styles can be established for a more harmonious family environment.
For instance, a parent dealing with insecurities originating from a tumultuous childhood may find themselves excessively checking their teenager's homework, seeking control and comfort in their child's academic success. This same teenager, under such persistent scrutiny, may develop stress and anxiety about their school performance.
Through EMDR therapy and counseling for teens, anxiety symptoms can be successfully managed and detrimental parenting styles rectified. This results in a healthier, happier, and more balanced family life for everyone involved.
How EMDR Can Help
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) therapy is not only for trauma survivors. In the context of parenting and homework, it can serve as an effective tool for parents. They can confront and manage their anxieties that may be influencing their parenting approach. EMDR can help to reprocess these anxious thoughts, shifting them from a place of fear to a mindset of understanding and empathy. This change can foster a more compassionate and patient parenting style.
On the other side, children who are dealing with the stress of academic pressure may also benefit from EMDR. Homework and academic challenges can sometimes be overwhelming, leading to an increased anxiety level. EMDR can assist in alleviating this distress, allowing them to approach their studies with a calm and composed mindset.
The technique involves the process of bilateral stimulation - typically through eye movements, tactile tapping, or auditory tones - while the individual recalls the stressful event. By doing this, EMDR works to modify the memories or fears associated with it, making them less distressing. For both parents and children, this can lead to a more positive and effective approach to homework. This will reduce the potential for battles and increase the potential for growth.
In essence, EMDR can help create a healthier learning environment by addressing and managing the root cause of academic-related stress and anxiety. By fostering a calm, patient, and understanding atmosphere, both parents and children can navigate the journey of education with increased resilience and confidence.

What is C-PTSD? How is it Similar and Different from Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)?
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and complex post-traumatic stress disorder (C-PTSD) are both neurobiological disorders that occur when someone experiences or witnesses a traumatic event. Examples include, but are not limited to, war or combat, natural disasters, physical or sexual assaults, and life-threatening accidents.
Almost all of us associate PTSD with veterans. We understand combat is gruesome on the body and devastating to the psyche. If only we look at the faces of our veterans when they return, it is clear that war is hell. We know, even without words, that they went through something far beyond the scope of normal human experience. In fact, generations before the term “post-traumatic stress disorder” became known, PTSD was known by other names: war neurosis, shell shock, soldier’s heart, or combat fatigue. Furthermore, much of the research, advocacy, awareness, and treatment options for PTSD have been through means such as the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs. Thus, it makes sense we as a collective society to visualize a soldier in battle when we think of PTSD.
However, many times PTSD is most prevalent in people who have experienced dangerous, life-altering events. It seems to be most frequent in survivors of sexual assault or those who went through or witnessed violent car accidents, both which involve powerlessness, danger, and terror. Furthermore, PTSD can occur in populations that often are forgotten to be traumatic, such as ICU stays.
It is believed most people will experience at least one traumatic event in their lives, and a fourth will develop PTSD. It is not known how many people live with Complex-Post Traumatic Disorder, C-PTSD.
Symptoms of PTSD

People who suffer from trauma may feel its impact for days; this is called acute trauma. If the symptoms continue for weeks or longer, and disrupt daily living, that is suggestive of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder, PTSD.
There are three types of PTSD symptoms:
Hyperarousal symptoms. People with PTSD may have sense-of-threat symptoms, as if they are on edge and hypervigilant of their environment. They can have a startled response such as jumpiness.
Re-experiencing symptoms. Nightmares and flashbacks are the hallmark symptoms of PTSD. The individual may “go through” the trauma again via memories, via sensory experiences and emotions. The individual may feel the same smells, sights, sounds of the trauma.
Avoidance symptoms. Those living with PTSD will participate in avoidance symptoms, as in avoiding triggers associated with the trauma. This is broad, and can include places, situations, people, or events (i.e., holidays). They may also attempt to drown the symptoms through self-medicating with alcohol or other substances.
What is Complex Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder?
C-PTSD is a multilayered version of PTSD involving prolonged or chronic attacks on an individual’s sense of safety, self-worth, and integrity. This is dissimilar to PTSD, which is the result of one traumatic event. The ongoing maltreatment causes a multitude of additional symptoms, which shape neuropsychological development such as personality.
C-PTSD results from situations of chronic powerlessness and a lack of control. This can be from long-standing domestic violence (whether experienced or witnessed), sex trafficking, or child maltreatment. However, it is most common in those who were subjected to child abuse or neglect at a very early age. This is prevalent if the harm is by a caregiver or other significant adult. Also, multiple traumas increase the risk of developing C-PTSD.
Symptoms of C-PTSD
People with C-PTSD have compounded symptoms of both PTSD and those from other mental health disorders. These may include the following:
Psychosomatic issues: Psychosomatic issues are physical issues without a medical explanation. This can be caused or worsened by a psychological reason such as stress. It is common for people with C-PTSD to have vague physical symptoms such as dizziness, chest pains, abdominal aches, and headaches.
Emotional flashbacks: A flashback is a vivid, intense experience in which a person will relive some parts of a trauma. Some people feel as if it is happening in the present. Stereotypically, people tend to think of the war veteran who is having a “movie-like” flashback in which the event unfolds again in its entirety. However, a flashback does not need to be so extreme – and usually they are not.

Difficulty regulating emotions: Those with C-PTSD may experience sharp, vivid emotions which can be inappropriate for the situation. These rapid shifts in mood can be misdiagnosed as bipolar disorder or borderline personality disorder, which can have similar features but are not the same.
Flat affect: People with C-PTSD may also have a flat affect, meaning they appear numb, somber, or emotionless to others. This body language can be misinterpreted by others, making people think the individual is feeling a certain way or is aloof. In truth, the person may have a rich, complex inner world of their emotions and be feeling very differently than how they are expressing themselves.
There are several reasons for a flat affect. One powerful reason is because the individual may not have witnessed emotional expression in their formative years, thus in turn they have been sharpened to be “flat” as an adult. To explain it plainly, imagine a primary caregiver not smiling at their baby. The baby mimics and responds to the caregiver by also not smiling. This is sharpening the baby to respond such a way going forward.
Other Symptoms of C-PTSD
A lack of emotional vocabulary: Finally, individuals with C-PTSD may have difficulty with articulating their emotions or they may not understand what they feel; that is, there is an absence of an emotional vocabulary. They may struggle in therapy when asked “what are you feeling?” and respond with “I don’t know” or they may describe a physiological feeling instead (i.e., tiredness, nausea). This is because in the context of prolonged trauma they had to adapt to shutting down their emotions to survive. For example, they may have been programmed in their earliest years to think “emotions are bad” because they were consistently invalidated or punished for emotional expression by their caregivers.
Dissociation: Dissociation happens to everyone. Dissociation is a sensation of feeling disconnected from oneself and the world through a sensory experience, thought, sense of self, or time. A person who dissociates may feel depersonalization (detached from their body) or derealization (feeling as if their surroundings are unreal). And at one time or another, all of us have dissociated. Getting lost in a daydream, forgetting the details of a car drive, or spacing out during a boring class lecture are all examples of dissociation.
When applied to trauma, dissociation is an innate coping mechanism. It is a protective action taken by the mind to let an individual survive a traumatic experience. At the time of the event, dissociation is beneficial, especially for children as they often lack insight and more sophisticated coping skills. However, the downside of dissociation is that when someone has dissociation and is at risk of developing C-PTSD or another trauma-related disorder, the dissociation does not resolve the trauma. In adulthood, the effects of dissociation can negate the ability to trust, form and maintain healthy relationships, and prioritize self-care. Through the phenomenon of mind-body separation, individuals may develop self-destructive behaviors such as ones that keep them dissociated (“I can’t tell when I’m feeling hungry, so I eat less than I should”) or ones to make them dissociate (“I drink alcohol to numb myself so I don’t have to feel my despair”).
Negative core beliefs: Individuals with C-PTSD may have the core belief “I am not safe” or “the world is unsafe.” Alternatively, they may have other core beliefs (“I am unlovable” or “I am not worthy of respect”, for example). These core beliefs are deeply ingrained, at the pool of their identities, which can mean the individual is unaware they even carry such beliefs until they develop more insight.
Relationship difficulties: Individuals with C-PTSD can struggle with developing and maintaining healthy relationships. Such individuals struggle with feeling able to trust others due to their traumatic histories; thus, they may isolate themselves or feel intensely uncomfortable with “opening up” to others. Or they may respond inappropriately in a social situation. Unfortunately, these factors only enhance their risk of disapproval or misunderstanding by others, which makes them more susceptible to social isolation or ridicule.
Additionally, people with C-PTSD are more susceptible to entering and remaining in abusive relationships – especially those who already experienced abuse.
Treatment for C-PTSD

C-PTSD is a treatable condition. However, clients (patients) should be cautious when selecting their therapist. The treatment of complex trauma is a specialty, and not all therapists have the knowledge, skills, or experience to adequately support those who have C-PTSD. Thus, it is encouraged to “screen” the therapist during the consultation session by asking for their background in treating C-PTSD. Much like we may make thoughtful, careful choices about our medical doctors, the same should be done for therapists too!
Ask the therapist about their intervention styles (treatment approaches) as well.
The following treatments are frequently utilized for C-PTSD treatment:
- Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) Therapy. In EMDR, the individual reflects on a trauma while following a bilateral stimulus that results in the eyes moving back-and-forth.
- Trauma processing therapies.
- Exposure therapy, in which individuals re-experience their traumas in a safe, controlled environment.
- Cognitive Behavior Therapy (CBT), which focuses on the relationship between cognitions (thoughts), emotions, physiological sensations, thereby changing the resulting behaviors.
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT), an off-set from CBT which also includes interpersonal effectiveness (relationship skills), emotional regulation, distress tolerance, and mindfulness.
- Cognitive Processing Therapy (CPT), a behavioral therapy that challenges and changes unhelpful beliefs associated with the traumatic events
Looking For a Therapist?
All of our counselors here at Long Island EMDR specialize in trauma work. We have a variety of sub-specialties within that including sexual assault, domestic violence, infertility, childhood abuse/neglect, loss of a loved one and bullying.
Wishing you healing and light,

Infidelity is a painful and traumatic experience that can leave lasting emotional scars for those involved. It can lead to feelings of betrayal, anger, and distrust, and can even result in the development of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). For those struggling to cope with the aftermath of infidelity, there is hope for healing and breaking the cycle of trauma. One powerful tool to overcome the trauma of infidelity is through PTSD therapy, specifically Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) therapy. In this blog post, we will explore how EMDR therapy can help individuals break free from the trauma of infidelity and move towards a path of healing and recovery.
Understanding Infidelity as a Trauma:
Infidelity is not simply a betrayal or breach of trust in a relationship. It can also be experienced as a deeply traumatic event that can leave lasting emotional scars. Understanding infidelity as a trauma involves recognizing the profound impact it can have on an individual's well-being.
When infidelity occurs, it shatters the foundation of trust that a relationship is built upon. The pain and shock of discovering a partner's unfaithfulness can cause intense emotional distress. Anxiety symptoms, such as constant worry, racing thoughts, and difficulty sleeping, may become overwhelming. Depression symptoms, including feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest in activities once enjoyed, can also arise. The shock and pain can be very difficult to overcome the trauma caused by infidelity.
In some cases, the trauma of infidelity can lead to the development of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). PTSD symptoms can include intrusive thoughts, nightmares, hypervigilance, and avoidance of anything that triggers memories of the infidelity.
Understanding infidelity as a trauma is crucial in order to address the deep emotional wounds it can cause. Recognizing the impact of infidelity as a traumatic experience allows individuals to seek the appropriate support and treatment for PTSD. Engaging in therapy, such as EMDR therapy, can help individuals process and heal from the trauma. This can enable them to regain a sense of safety, trust, and self-worth.
The Connection Between PTSD and Trauma Bonding:

The connection between PTSD and trauma bonding is a complex and intertwined one. Trauma bonding refers to the psychological phenomenon in which a person forms an intense emotional attachment to an abusive or betraying partner. This bond can make it incredibly difficult for the victim to break free from the relationship, despite the harm they are experiencing
In the context of infidelity, trauma bonding can occur when the betrayed partner develops a deep emotional attachment to their unfaithful spouse or partner. This attachment is often rooted in feelings of fear, dependency, and a distorted belief that the unfaithful partner is the only source of love and support. These intense emotional bonds can be incredibly challenging to sever, even in the face of ongoing emotional and psychological harm.
For individuals who have experienced infidelity and developed trauma bonding, the combination of PTSD and trauma bonding can be particularly challenging to overcome. The symptoms of PTSD, such as intrusive thoughts, nightmares, and hypervigilance, can reinforce the trauma bond and make it even harder for the individual to break free.
Addressing trauma bonding in therapy is essential for individuals seeking treatment for PTSD related to infidelity. Therapists trained in trauma-focused approaches, such as EMDR therapy, can help individuals understand and process the trauma bond. By addressing both the PTSD symptoms and the trauma bond, individuals can work towards breaking free from the cycle of trauma and begin the journey towards healing and recovery.
In the next section, we will explore how EMDR therapy can be a potential solution for trauma-related issues, including trauma bonding in the context of infidelity.
EMDR Therapy: A Potential Solution for Trauma-Related Issues:

EMDR therapy, or Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing therapy, has shown great promise as a potential solution for trauma-related issues, including the emotional wounds caused by infidelity. This type of therapy focuses on reprocessing traumatic memories and reducing the distress associated with them.
In the context of infidelity, EMDR therapy can help individuals struggling with anxiety and depression symptoms. Anxiety treatment is a significant component of EMDR therapy, as it addresses the constant worry, racing thoughts, and difficulty sleeping that often accompany the trauma of infidelity. By using techniques such as bilateral stimulation, which involves moving the eyes back and forth or tapping on the body, individuals can process and desensitize their traumatic memories, leading to a reduction in anxiety symptoms.
Similarly, EMDR therapy can also be effective in addressing depression symptoms. By reprocessing the traumatic memories associated with infidelity, individuals can begin to regain a sense of self-worth and find healing from the profound sadness and loss of interest in once-enjoyed activities. The therapy process allows individuals to process the emotions connected to the trauma and replace negative beliefs about themselves with more positive and empowering ones.
Through the power of EMDR therapy, individuals can overcome the emotional trauma left by infidelity and begin their journey towards healing and recovery. It is important to seek a trained and experienced EMDR therapist who can guide and support individuals through this transformative therapy process. With dedication and perseverance, individuals can break free from the cycle of trauma and move towards a brighter and more fulfilling future.
The Role of EMDR Intensives in Overcoming Trauma:
EMDR (Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing) therapy is a powerful tool in overcoming trauma, including the emotional wounds caused by infidelity. But what role do EMDR intensives play in the journey towards healing?
EMDR intensives are extended therapy sessions that allow individuals to delve deeper into their trauma and work through it in a concentrated period of time. These sessions typically last several days and involve multiple therapy sessions each day. The length and intensity of EMDR intensives allow for a more comprehensive and focused approach to trauma processing.
One of the main benefits of EMDR intensives is the ability to establish and maintain momentum in the healing process. Unlike traditional therapy, which may only occur once a week or every few weeks, EMDR intensives provide consistent and continuous support. This helps individuals stay engaged in the healing process and make significant progress in a shorter time frame.
EMDR intensives also allow individuals to immerse themselves fully in the therapeutic experience. By dedicating a block of time solely to healing, individuals can more effectively process and integrate their traumatic experiences. This deep level of focus can facilitate breakthroughs and create lasting change.
Another advantage of EMDR intensives is the opportunity for the therapist and client to develop a stronger therapeutic relationship. Spending extended time together allows for a deeper level of trust and understanding to develop, which can enhance the therapeutic process.
While EMDR intensives can be intense and emotionally challenging, they offer a unique and powerful approach to overcome trauma from infidelity. They provide a space for individuals to work through their pain, process their emotions, and ultimately, move towards a path of healing and recovery. Through the support and guidance of an experienced EMDR therapist, individuals can break free from the cycle of trauma and embrace a brighter future.
Embracing the Journey Towards Healing:

Recovering from the trauma of infidelity is not an easy journey, but it is possible. It requires a commitment to healing and a willingness to embrace the journey towards healing. One important aspect of this journey is seeking out appropriate treatment, such as EMDR therapy, to address the emotional scars left by infidelity and break free from the cycle of trauma.
Anxiety treatment is a significant component of EMDR therapy, as it helps individuals manage the constant worry, racing thoughts, and difficulty sleeping that often accompany the trauma of infidelity. Through EMDR therapy, individuals can learn effective coping mechanisms and strategies to reduce anxiety symptoms, regain a sense of control, and restore a sense of safety.
Additionally, embracing the journey towards healing involves a commitment to self-care and self-compassion. This may involve engaging in activities that bring joy and promote emotional well-being, such as exercise, spending time in nature, or practicing mindfulness and relaxation techniques.
It is also important to seek support from trusted friends, family, or a therapist who specializes in trauma and infidelity. Connecting with others who have experienced similar pain and trauma can provide a sense of validation and understanding, while also offering the opportunity for shared healing and growth.
Finally, embracing the journey toward healing requires patience and self-forgiveness. Healing takes time, and setbacks may occur along the way. It is important to remember that healing is not linear, and that progress can be made even in the face of challenges.
By embracing the journey towards healing, individuals can break free from the cycle of trauma and create a brighter future filled with resilience, strength, and a renewed sense of self.